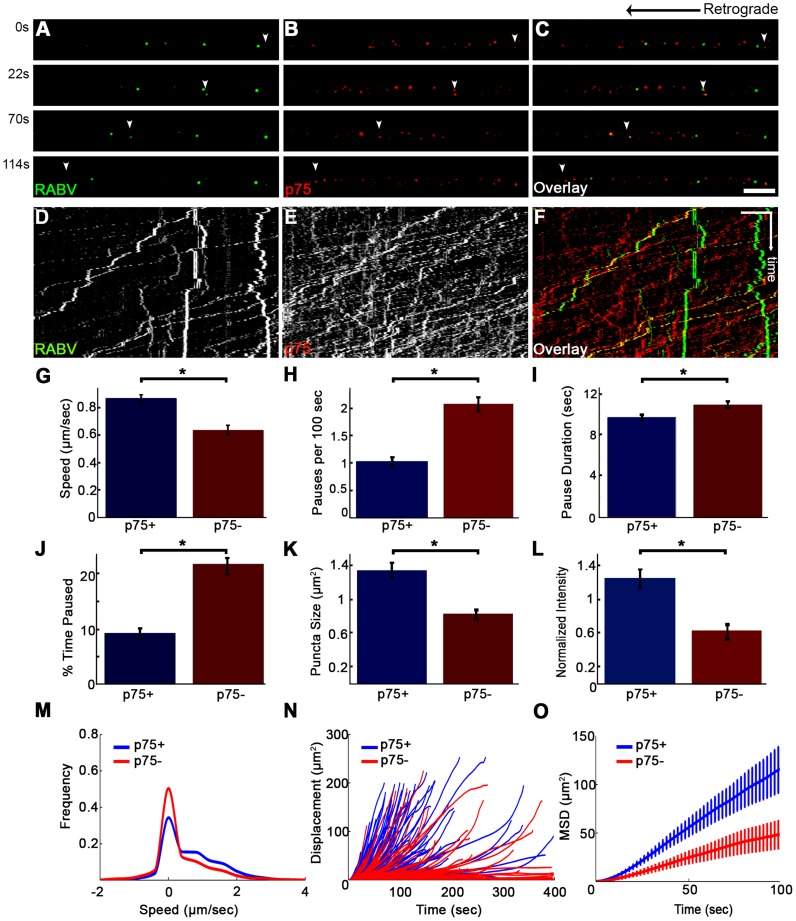
Figure 8. RABV travels faster and is more directed when transported with p75NTR.
(A–C) Multi-channel live imaging of EGFP-RABV 2 hours after addition to distal axon compartment of DRG explant previously treated with a fluorescent antibody against p75NTR. Arrowheads: p75NTR-positive RABV puncta, scale bar = 10 µm. (D,E) Kymographs of and P75NTR extracted from time lapse depicted in (A–C). (F) RABV-only tracks (green) are less directed than RABV-p75NTR tracks (yellow), as shown when overlaying corresponding kymographs. Vertical scale bar = 5 µm, horizontal scale bar = 40 seconds. (G–O) Characterization of directed RABV puncta, transported with and without p75NTR, n = 184 and n = 122, respectively. (G) RABV presents higher speeds when transported with p75NTR, due to less frequent (H) and shorter pauses (I). Overall RABV-p75NTR spent less time paused on average (J), Diameter and intensity measurements revealed that RABV puncta positive for p75NTR were larger (K) and had higher intensity levels (L) than p75NTR-negative puncta. (M–O) p75NTR positive puncta (blue) are faster, more directed and present higher displacements over time, compared to p75NTR negative puncta (red), illustrated by distribution of instantaneous velocities in (M) (RABV+p75: n = 8051 events; RABV-p75: n = 7423 events) displacement plotted over time (N) and mean square displacement (O). Data is pulled from two separate experiments, error bars represent SEM. *p<0.05.