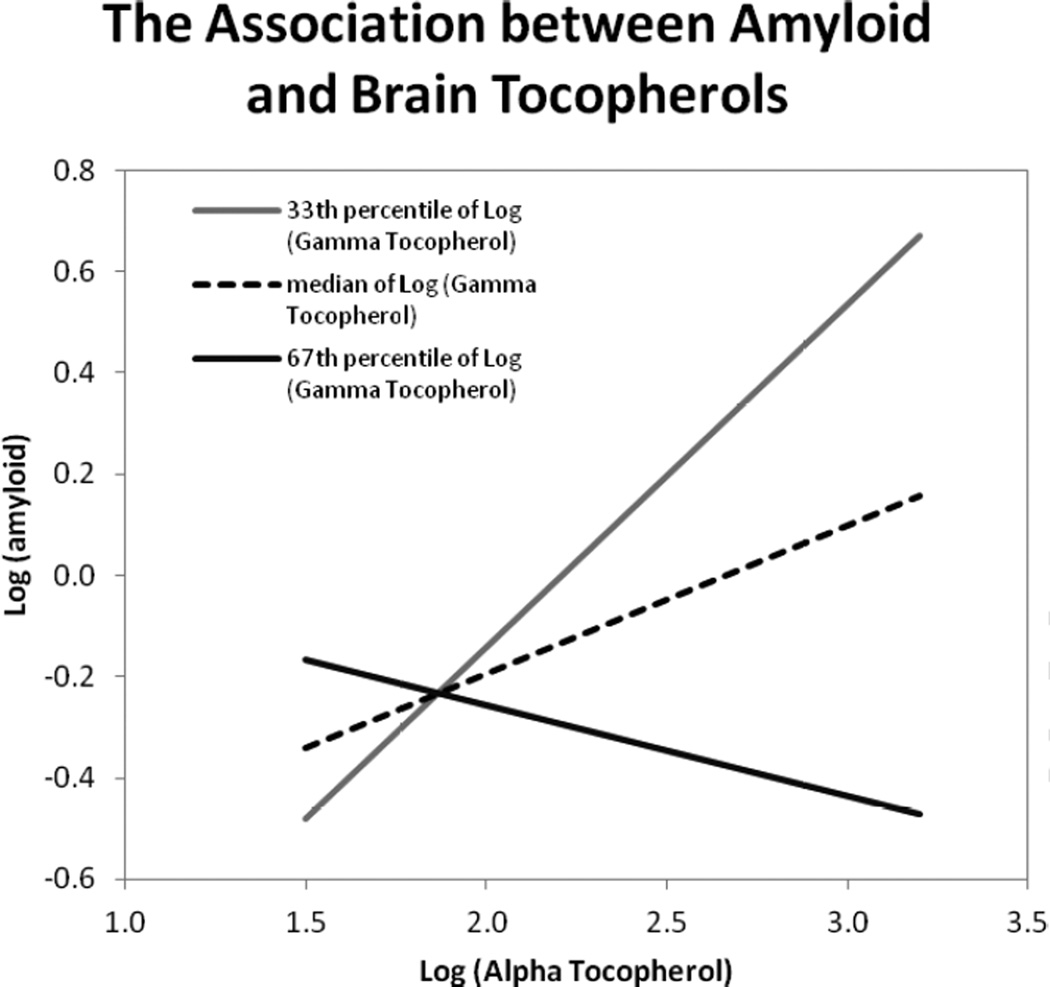
Figure 2.
Statistical interaction effect between α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol on amyloid load based on an age-adjusted linear regression model with log10 (α-tocopherol) and log10 (γ-tocopherol) modeled as continuous variables in pmol/mg protein and their multiplicative term (p-value for interaction=0.03). The lines reflect the association between amyloid load and alpha tocopherol at three different values of gamma tocopherol: log10 =1.7 at the 33rd percentile (grey), log10 =1.8 at the 50th percentile (dotted), and log10 =1.9 at the 67th percentile (black). Higher levels of α-tocopherol were associated with increased amyloid load except when the levels of γ-tocopherol were also high, at which point higher levels of α-tocopherol were associated with lower amyloid levels.