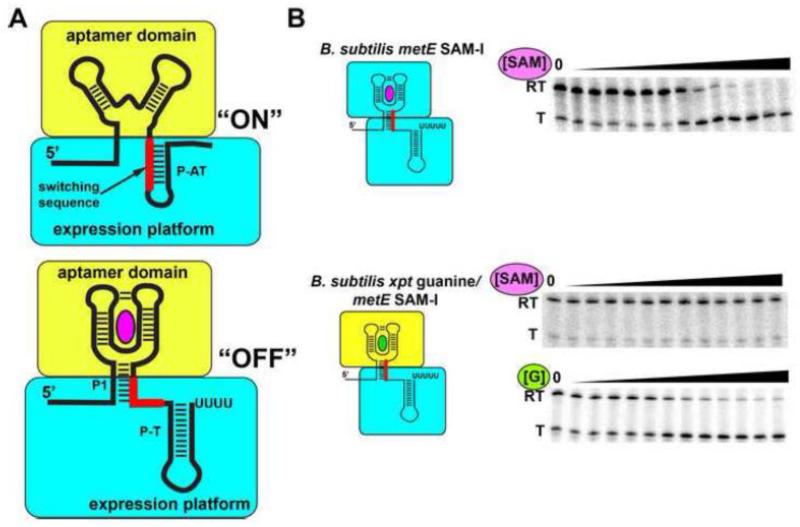
Figure 6. Synthesis of chimeric riboswitches from biological parts.
(A) In order for the expression platform to be used as a modular part, all of the sequences required for the alternative secondary structural switch must be distinct from the sequence that defines the minimal aptamer domain (yellow). In many riboswitches, the key element is the “switching sequence” (red), the region of the expression platform (cyan) shared between the two alternative structures. (B) An example of a functional chimeric riboswitch. The top shows the wild type B. subtilis metE SAM-responsive riboswitch undergoing transcriptional attenuation as a function of increasing ligand concentration in a single-turnover transcription assay (RT, read through product; T, terminated product). The middle shows that a chimera of the B. subtilis xpt-pbuX guanine binding aptamer domain and the B. subtilis metE expression platform is no longer SAM-responsive, but is strongly responsive to guanine (bottom). Figure adapted from (118).