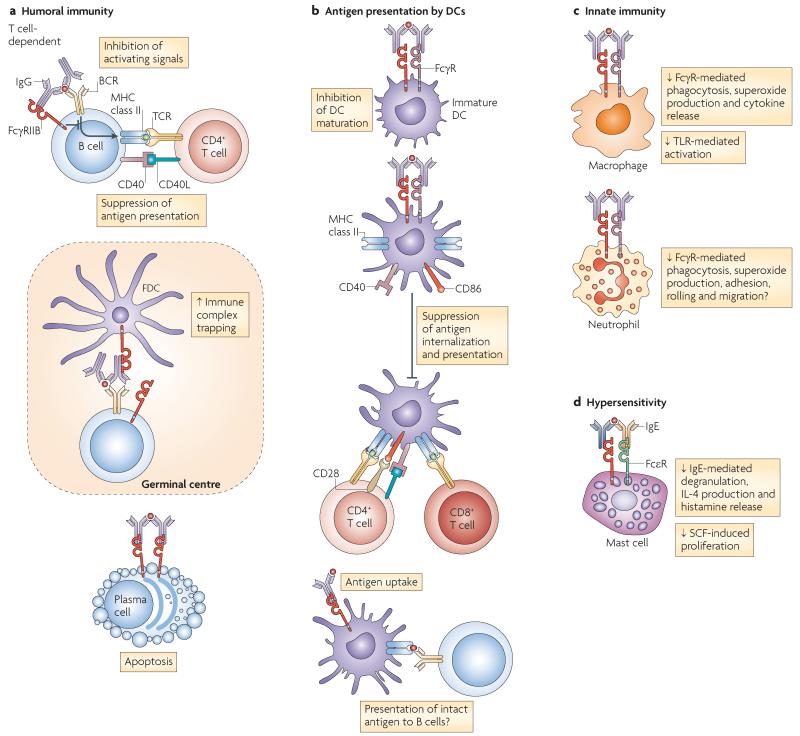
Figure 2. The functions of FcγRIIB.
a | Fc receptor IIB for IgG (FcγRIIB) has an important role in controlling humoral immunity by regulating B cell activation, localization of B cells in the germinal centres, as well as plasma cell survival. FcγRIIB regulates B cell activation by increasing the B cell receptor (BCR) activation threshold and suppressing B cell-mediated antigen presentation to T cells. Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) express FcγRIIB, which is thought to be important for trapping immune-complexed antigen for presentation to germinal centre B cells. The absence of FcγRIIB on germinal centre FDCs results in impaired antibody and memory responses. Terminally differentiated plasma cells express little or no BCR but express high levels of FcγRIIB, and cross-linking FcγRIIB with immune complexes in vitro can induce apoptosis. b | FcγRIIB influences antigen presentation by inhibiting FcγR-dependent internalization of immune-complexed antigen by DCs, as well antigen presentation to both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (cross-presentation). FcγRIIB is also thought to provide a basal level of inhibition to DC maturation, as blockade of immune complex binding to FcγRIIB results in DC maturation and type I interferon production. There is also a possibility that FcγRIIB may deliver intact antigen to a non-degradative compartment, allowing its recycling to the cell surface where it could interact with the BCR and activate B cells. c | FcγRIIB can also influence innate immunity: in macrophages, FcγRIIB cross-linking inhibits FcγR-mediated phagocytosis and cytokine release (including tumour necrosis factor, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-1α), as well as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated activation. In neutrophils, cross-linking of activating FcγRs results in phagocytosis, superoxide production and enhanced neutrophil adhesion, rolling and migration, all of which are probably inhibited by ligating FcγRIIB. d | FcγRIIB also inhibits IgE-induced mast cell and basophil degranulation, thus contributing to hypersensitivity responses. FcεR, Fc recpetor for IgE; SCF, stem cell factor.