FIGURE 8.
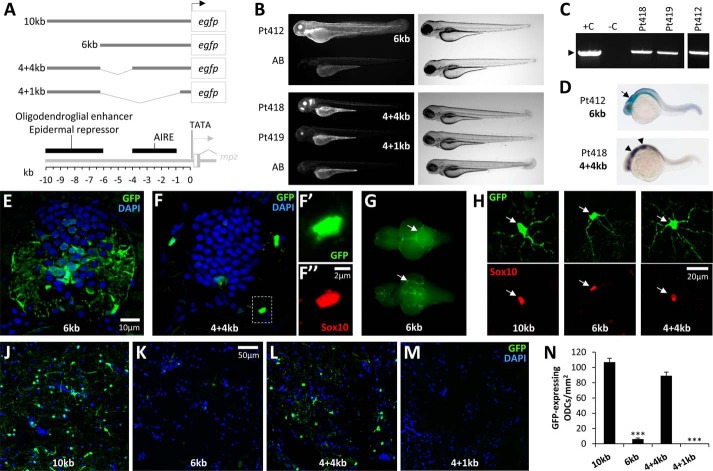
An oligodendroglial enhancer is located in the mpz upstream regulatory region. A, a panel of deletion mutants was constructed in order to localize the AIRE within the 10-kb mpz cis-regulatory construct shown in Figs. 2–7. The constructs shown schematically were tested in transient assays in zebrafish larvae and used to generate stable transgenic zebrafish lines. The map below summarizes the locations of key elements in the mpz regulatory region that were delineated in this study, including the TATA motif and transcription start site, AIRE, and upstream oligodendroglial enhancer/epidermal repressor sequences. B, epifluorescence micrographs (GFP channel; left panels) and light micrographs (right panels) showing stable Tg(mpz[6kb]:egfp) (Pt412; top panels), Tg(mpz[4+4kb]:egfp), and Tg(mpz[4+1kb]:egfp) (Pt418 and Pt419; bottom panels) zebrafish larvae at 72 h postfertilization. C, genotyping data confirming stable integration of the mpz:egfp transgenes in F3 generation zebrafish from lines Pt412, Pt418, and Pt419. Tail fin genomic DNA was subjected to PCR analysis as shown in Fig. 2B. Lane 1, positive control (+C), wild-type genomic DNA spiked with transgene plasmid; lane 2, negative control (−C), wild-type genomic DNA; lanes 3–5, genomic DNA from Pt418 (lane 3), Pt419 (lane 4), and Pt412 (lane 5, from a separate gel run in parallel). The expected PCR product is indicated by an arrowhead. D, whole mount RNA in situ hybridization using a cRNA probe to egfp and a chromogenic reaction with a blue/purple product was employed to show the early developmental expression of the 6-kb (top) and 4 + 4-kb (bottom) mpz constructs. E, transverse section of the spinal cord from a Tg(mpz[6kb]:egfp) zebrafish at 7 dpf labeled for GFP (green) and DAPI (blue). F, transverse section of the spinal cord from a Tg(mpz[4+4kb]:egfp) zebrafish at 7 dpf. Single confocal planes of the boxed area are shown in F′ and F″ at high magnification (green, GFP; red, Sox10; blue, DAPI). G, GFP epifluorescence photomicrographs are shown of a freshly dissected whole brain from a Tg(mpz[6kb]:egfp) zebrafish (dorsal view above, ventral view below). The arrows indicate bright GFP fluorescence on the meningeal surface of the brain. H, confocal micrographs of single GFP-expressing oligodendrocytes from the hindbrain of individual Tg(mpz:egfp) zebrafish lines, expressing a GFP reporter under different mpz regulatory fragments as indicated (see A). Top row, GFP (green); bottom row, Sox10 (red). The arrowheads show the position of the GFP-expressing cell bodies, confirming that the same cells were also Sox10-immunoreactive. The scale for all six panels is shown in the bottom right panel. J–M, fluorescence micrographs of the medulla oblongata of individual Tg(mpz:egfp) zebrafish lines, expressing a GFP reporter under different mpz regulatory fragments (see A). Sections are labeled for GFP (green) and DAPI (blue). The scale for all four panels is shown in the second panel. N, GFP-expressing oligodendrocytes were quantified in the medulla oblongata of Tg(mpz:egfp) zebrafish, expressing a GFP reporter under different mpz regulatory fragments as shown in A. Graphs show mean and S.E. (error bars). ***, p < 0.0001 compared with animals expressing the 10-kb mpz:egfp construct (one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc test).