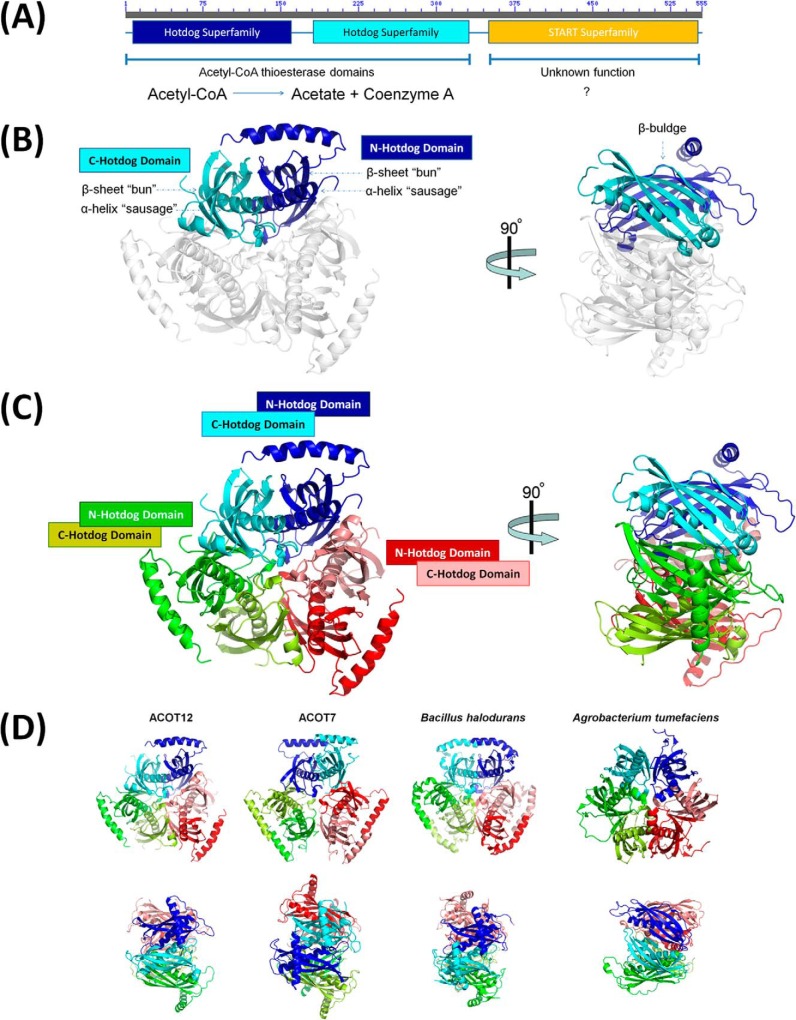
FIGURE 1.
Structure of ACOT12. A, domain architecture of ACOT12 comprised of two hotdog domains and C-terminal START domain. B, structure of the ACOT12 double hotdog domain protomer shown in schematic representation, with each hotdog domain in dark and light shades of the same color for each protomer. A 90° rotation highlights the presence of a β-bulge induced at each dimer interface. C, structure of the ACOT12 quaternary arrangement comprised of a trimer of hotdog dimers. D, structures of thioesterases containing the same hexameric arrangement built from either three double hotdog dimers (eukaryotes) or six single hotdog monomers (prokaryotes). Shown are structures of the thioesterase domains from B. halodurans (PDB code 1VPM (21)) a single hotdog fold thioesterase that forms a hexamer; the full length structure of ACOT7 (PDB codes 2Q2B and 2V1O (34)) and the structure of the double hotdog thioesterase from A. tumefaciens (PDB code 2GVH), which forms a back-to-back protomer.