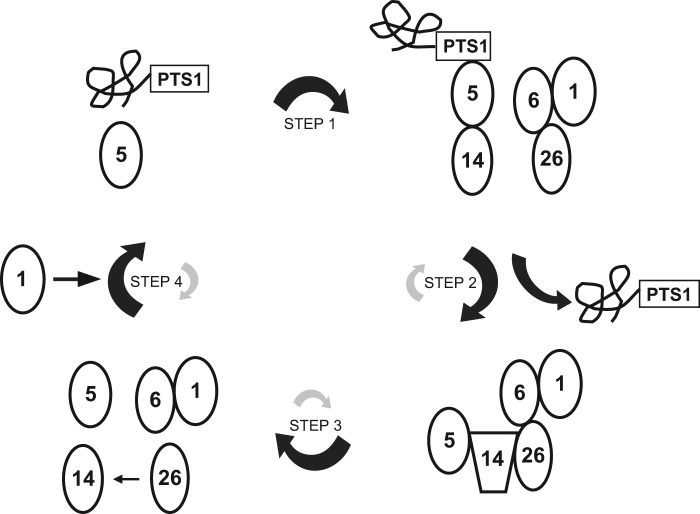
FIGURE 10.
A model for the role of Pex26p in Pex5p shuttling. Pex5p-PTS1 complexes formed in the cytosol dock onto Pex14p (step 1). PTS1 proteins are released at the inner surface and/or inside of peroxisomes, and then conformational change of Pex5p enables Pex14p·Pex5p complexes to interact with Pex26p (step 2). Pex14p is dissociated from Pex26p by chaperon-like activities coupled with ATP hydrolysis of Pex1p·Pex6p (step 3). The disassembled Pex14p releases PTS1-unloaded Pex5p, and then Pex5p shuttles back to the cytosol (step 4), where cytosolic Pex1p modulates the oligomeric forms of Pex5p.