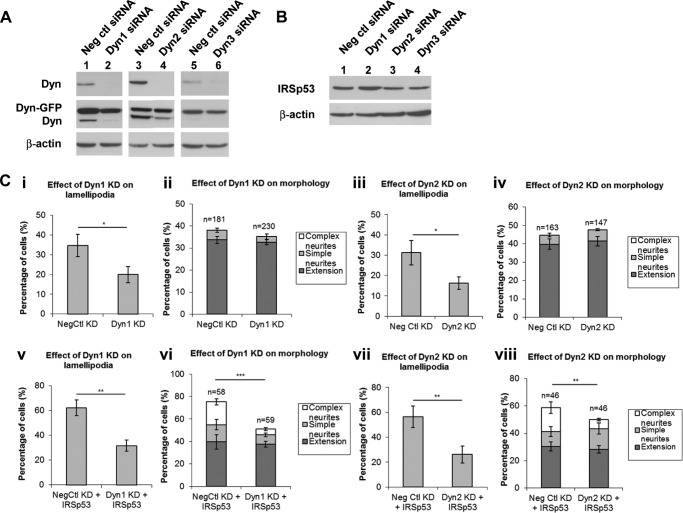
FIGURE 3.
Dyn1 is required for the IRSp53 phenotype. A, Dyn1–3 expression was monitored with siRNA addition. The rescued cDNA constructs encoding for exogenous Dyn-GFP were resistant against knockdown (KD) by the mouse Dyn-specific siRNA sequences. N1E-115 cells, with or without Dyn-GFP transfection, were subjected to KD with negative control (Neg ctl) siRNA (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or Dyn-specific siRNA (lanes 2, 4, and 6). Rescue experiments were performed by transfecting cells human Dyn1-GFP cDNA for 24 h and rat Dyn2- or 3-GFP for 48 h after siRNA addition. B, IRSp53 expression was not significantly perturbed under Dyn KD. The cDNA encoding for IRSp53 was transfected at 24 and 48 h after siRNA introductions (lanes 2–4) for Dyn1, and Dyn2 or Dyn3, respectively. C, bar charts show quantitative analysis of lamellipodia (panels i, iii, v, and vii) and outgrowths (panels ii, iv, vi, and viii) upon Dyn KD, with or without IRSp53 transfection. Quantitative analysis of cell morphology was determined by the percentage of cells containing neurites (extensions greater than one body length) and/or complex neurites (extensions with multiple branch points). Values were expressed as average ± S.D., n as indicated. Three independent experiments were performed, and the scores for each were pooled for statistical analysis with Student's t test. Asterisk denotes values with significant difference, i.e. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.