FIGURE 2.
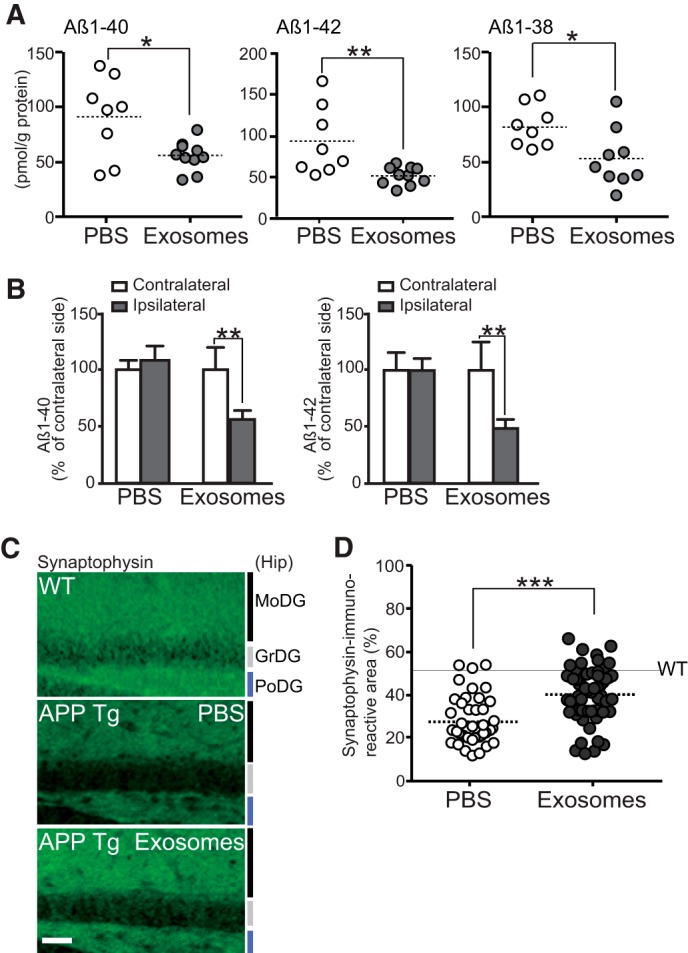
Intracerebral administration of N2a-exosomes induces Aβ clearance. Exosomes (12 μg of protein/PBS/day) or vehicles were continuously infused into lateral ventricle (A, C, and D) or right hippocampus (B) of APP mice (4 months) for 14 days. A, after the infusion, hippocampal levels of Aβ were measured by ELISA (n ≥ 5 animals per group; mean ± S.D.; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; Student's t test). B, hippocampal Aβ levels in ipsilateral and contralateral side were measured by ELISA. Values are represented as the percentages of the Aβ levels in the contralateral side (PBS, n = 3; exosome, n = 4; mean ± S.D.; **, p < 0.01; Student's t test). C, representative hippocampal sections of exosome- or vehicle-infused APP mice or age-matched nontransgenic controls stained with antibody against synaptophysin. MoDG, molecular dentate gyrus (DG); GrDG, granular DG; PoDG, polymorph DG. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, densities of synaptophysin-positive presynaptic terminals in the hippocampal sections in C were quantified (5 sections/mouse, 5 mice per group). Data presented are the mean ± S.D. ***, p < 0.001.
