FIGURE 3.
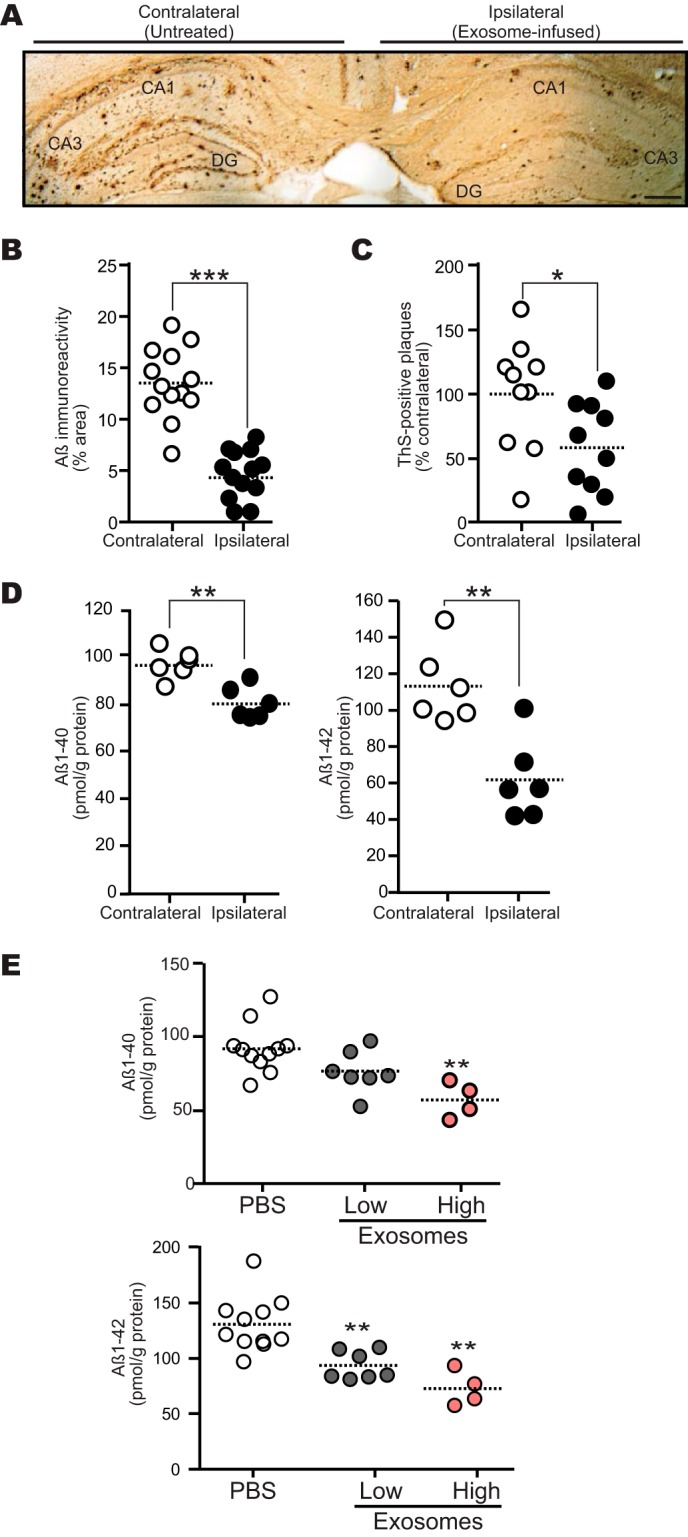
Intracerebral administration of N2a-exosomes reduces Aβ deposition. Exosomes (12 μg of protein/PBS/day) were continuously infused into the hippocampus (A–D) or lateral ventricle (E) of 13-month-old APP mouse for 14 days. A, representative image of APP mouse hippocampal section stained with antibody against Aβ (4G8). DG, dentate gyrus. Scale bar, 200 μm. B, Aβ-immunopositive areas in each hippocampal region were quantified (n = 4 animals, 3 or 4 sections per mouse brain; ***, p < 0.001). C, the number of thioflavin-S (ThS)-positive plaques in each hippocampus was determined (n = 4 animals, 2 or 3 sections per a brain; *, p < 0.05). D, the levels of hippocampal Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 were measured by ELISA (n = 3 animals, assayed in duplicate; **, p < 0.01). E, exosomes (low, 12 μg of protein/PBS/day; high, 24 μg of protein/PBS/day) were infused. Hippocampal Aβs were measured by ELISA (n ≥ 4 animals per group; **, p < 0.01 compared with PBS).
