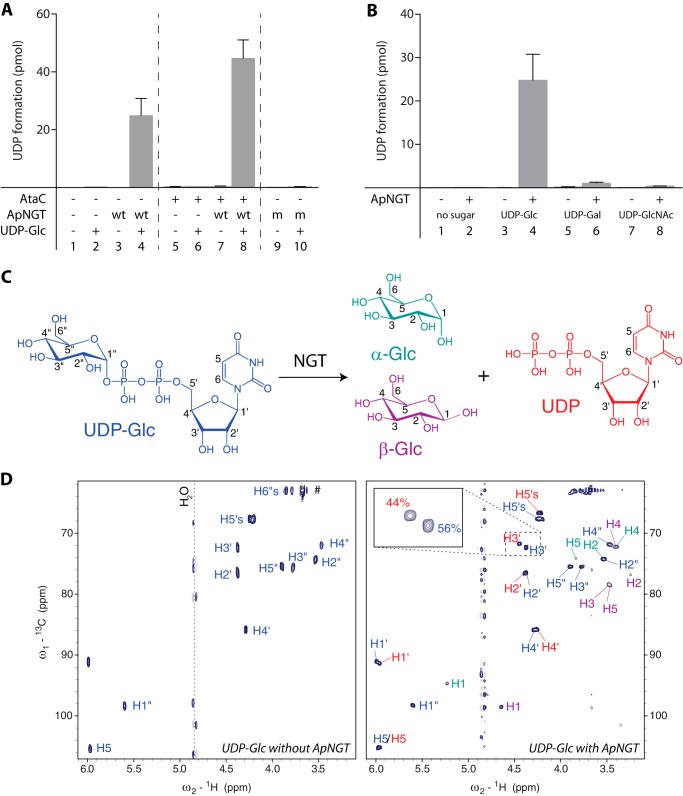
FIGURE 1.
ApNGT hydrolyzes nucleotide-activated sugars. A, substrate protein AtaC1866–2428 was incubated with UDP-Glc and purified ApNGT for 3 h at 30 °C and free UDP was determined using the bioluminescent UDP-Glo glycosyltransferase assay. Note that UDP is also formed in the absence of substrate protein but not in the absence of ApNGT or UDP-Glc or by the catalytically inactive ApNGT-K441A mutant. B, hydrolysis of different UDP-activated sugars. ApNGT hydrolyzed UDP-Glc and UDP-Gal (∼25 times slower) but not UDP-GlcNAc. C, schematic representation of UDP-Glc hydrolysis reaction. The color code corresponds to the color label in the NMR spectra. Numbers indicate the nomenclature of the protons. D, 1H-13C heteronuclear single-quantum coherence spectrum of 1 mm UDP-Glc measured with 2 scans at 293 K (left) and 1H-13C heteronuclear single-quantum coherence spectrum of 1 mm UDP-Glc after incubation for 20 h with 10 μm NGT measured with 32 scans at 293 K (right). The labels of the different reaction products are color coded corresponding to panel C. The assigned chemical shifts of UDP-Glc and UDP match previously reported values (45).