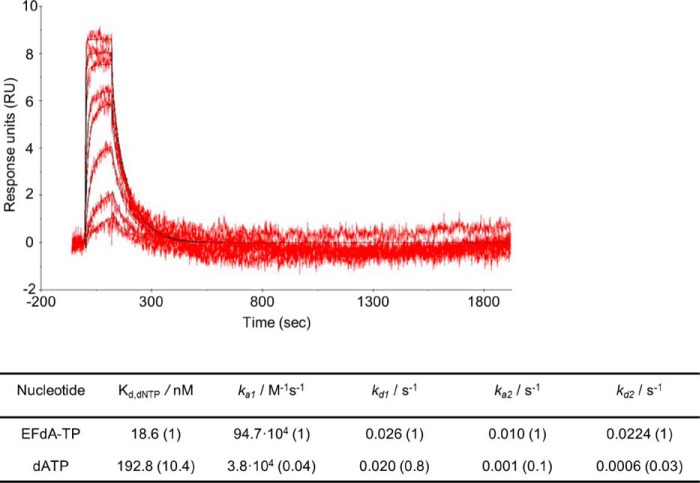
FIGURE 3.
SPR to determine the kinetic constants of EFdA-TP and dATP binding to HIV-1 RT. Nucleotide binding was performed by using RT covalently cross-linked to Td37/Pd20, which has a 5′-biotinylated DNA template and a ddGMP incorporated at the primer. The RT-DNAddGMP complex was immobilized on a streptavidin sensor chip, and increasing concentrations of dATP or EFdA-TP were flowed to allow nucleotide association and dissociation. A two-state reaction protocol was used to analyze the SPR data, which assume a 1:1 binding of substrate (EFdA-TP or dATP) to an immobilized ligand (RT) followed by a conformational change (closing of fingers subdomain) to form a stable complex. The graph shows the association and dissociation of EFdA-TP over time. This analysis generated the following kinetic values: ka1, the association rate constant for substrate binding; kd1, the dissociation rate constant for substrate from the complex; ka2, the forward rate constant for the conformational change; kd2, the reverse rate constant for the conformational change; and Kd, the overall equilibrium dissociation constant, which for this type of two-state reaction protocol is defined by Kd = (kd1/ka1)·(kd2/(kd2 + ka2)). The -fold change of the various constants is shown in parentheses.