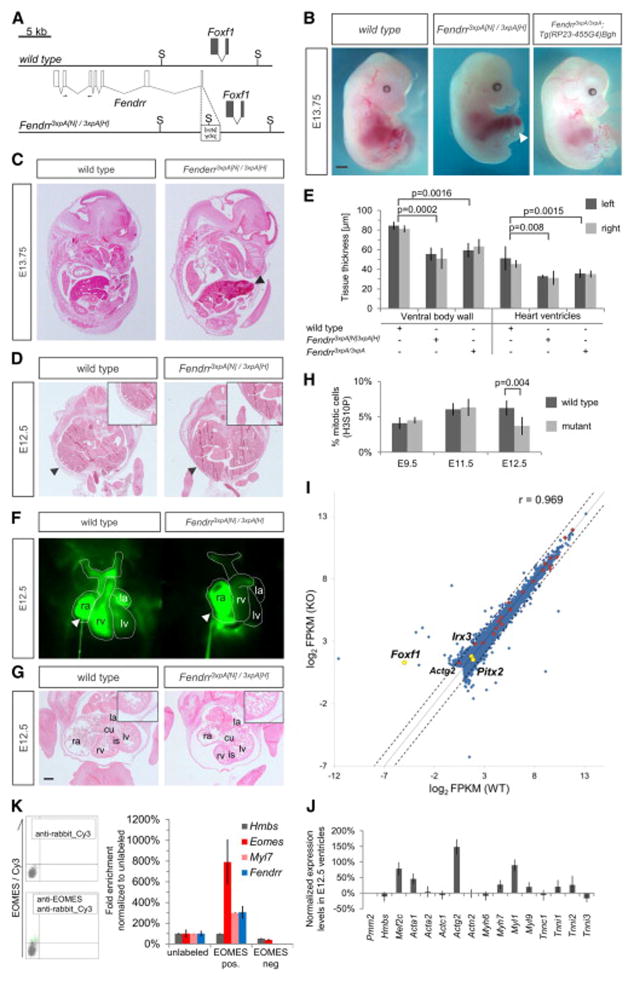
Figure 2. Heart and body wall development are impaired in mutants lacking Fendrr transcripts.
(A) Schematic showing the wild type (upper) and targeted (lower) Fendrr-Foxf1 genomic regions; the first exon of Fendrr was replaced with a 3xpA stop cassette by gene targeting in order to prevent transcription of the gene. Arrows indicate the position of primers used for real-time qPCR analysis. (B) E13.75 embryos derived by tetraploid complementation from wild type or homozygous Fendrr mutant ES cells including the neighbouring selection cassettes (Fendrr3xpA[N)/3xpA(H]). In mutant embryos the ventral body wall is perforated by umbilical vessels and parts of the liver; the presence of selection cassettes had no visible effect on the phenotype (see also Figure S3A and S3B). The phenotype was rescued by expression of Fendrr from a modified BAC transgene (Tg(RP23-455G4)Bgh). Note that the tail and limbs have been removed to better observe the ventral malformations. Scale bar: 1 mm. (C) Transverse histological sections of E12.5 wild type and mutant embryos at the mid-trunk level. The body wall of E12.5 mutant embryos is significantly thinner than that of wild type embryos (arrowheads and inlet), leading to perforation by the liver and umbilical vessels at later stages. (D) Transverse histological sections of E12.5 wild type and mutant embryos at the chest level. The thickness of the ventricular wall in the mutant heart is significantly reduced as compared to wild type (inlet). Abbreviations: rv, right ventricle; is, interventricular septum; cu, atrio-ventricular endocardial cushion; la, left atrium; lv, left ventricle. Scale bar: 200 μm. (E) Tissue thickness was measured from Eosin-stained transverse sections of E12.5 wild type and homozygous mutant embryos. Measurements were taken on either side using Zeiss AxioVision software, and values from both sides were combined for paired t-test analysis. Mean +/− s.d. are shown (n=3). (F) Percentage of mitotic cells (H3S10P) in heart ventricles determined on two distinct sections each of three different embryos. Paired t-test analysis and mean +/− s.d. are shown (n=3).