Figure 1. Double-retina specimen holder.
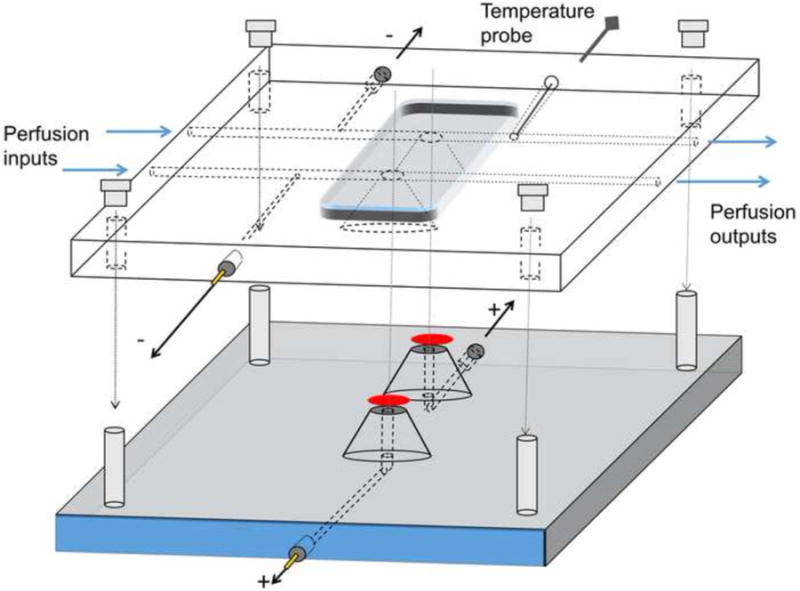
The bottom part has two domes topped with filter paper supporting the retinas (red ovals). Electrode channels filled with physiological solution allow electrical contact to the ganglion cell side of the retinas. Two pellet electrodes with custom-build housings (see text) are thread-connected. The top part has individual perfusion channels for each retina. Electrical connection to photoreceptor side of the retinas is achieved through narrow channels that are connected to the perfusion channels. Similar electrodes as in the bottom part are thread-connectable. After placing the dissected retinas on the domes, the top part is clamped tightly to the bottom part with permanent screws in the bottom part and nuts on the top. O-rings (not shown in the Figure) around the domes prevent perfusion solution leaks.
