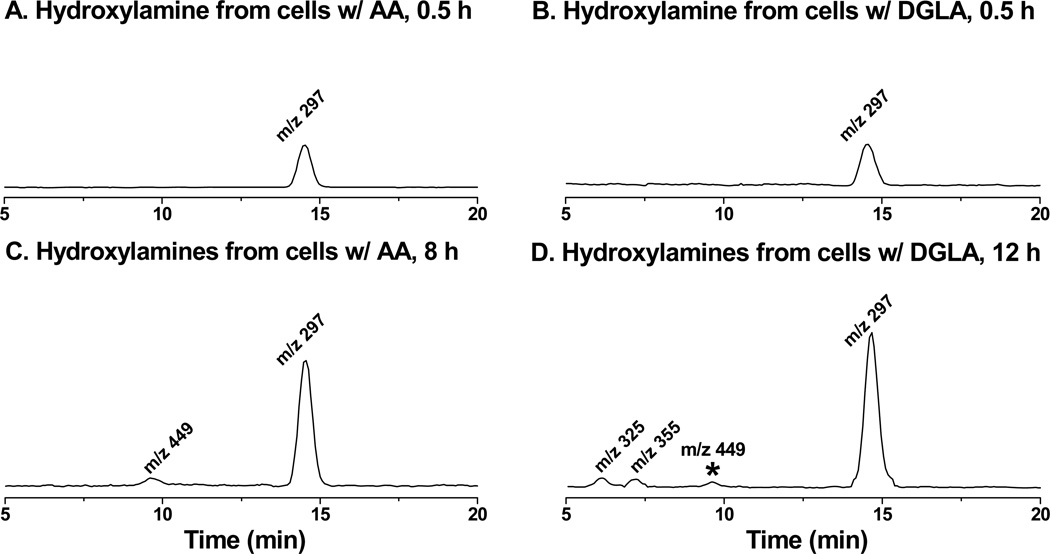
Fig. 2.
LC/MS chromatogram (EICs) of hydroxylamines formed from cellular COX-catalyzed PUFA peroxidation. HCA-7 colony 29 cells were cultured in normal culture media supplemented with PUFAs and POBN as described in Materials and Methods. At the experimental time points, cell culture medium together with cells that were scrubbed and homogenized was mixed with a stop solution of ACN (1:1, v/v). The hydroxylamines were then extracted by SPE, condensed, and then subjected to LC/MS and LC/MS2 analysis as described in Materials and Methods. (A) EIC of m/z 297 ion as reduced POBN adduct of ●C6H13O formed from COX-catalyzed peroxidation in cells treated by AA at 30 min; (B) EIC of m/z 297 formed in COX-catalyzed peroxidation from cells treated by DGLA at 30 min; (C) EIC of m/z 297 and m/z 449 (reduced POBN adduct of ●C14H21O4) formed in COX-catalyzed peroxidation from cells treated by AA at 8 h; and (D) EIC of m/z 297, m/z 325 and m/z 355 (reduced POBN adducts of ●C7H13O3 and ●C8H15O3, respectively) formed in COX-catalyzed peroxidation from cells treated by DGLA at 12 h. Note, the asterisked m/z 449 ion in Fig 2D represents the reduced POBN adduct of ●C6H13O generated from COX-catalyzed AA peroxidation where DGLA is converted to AA by Δ-5 desaturase.