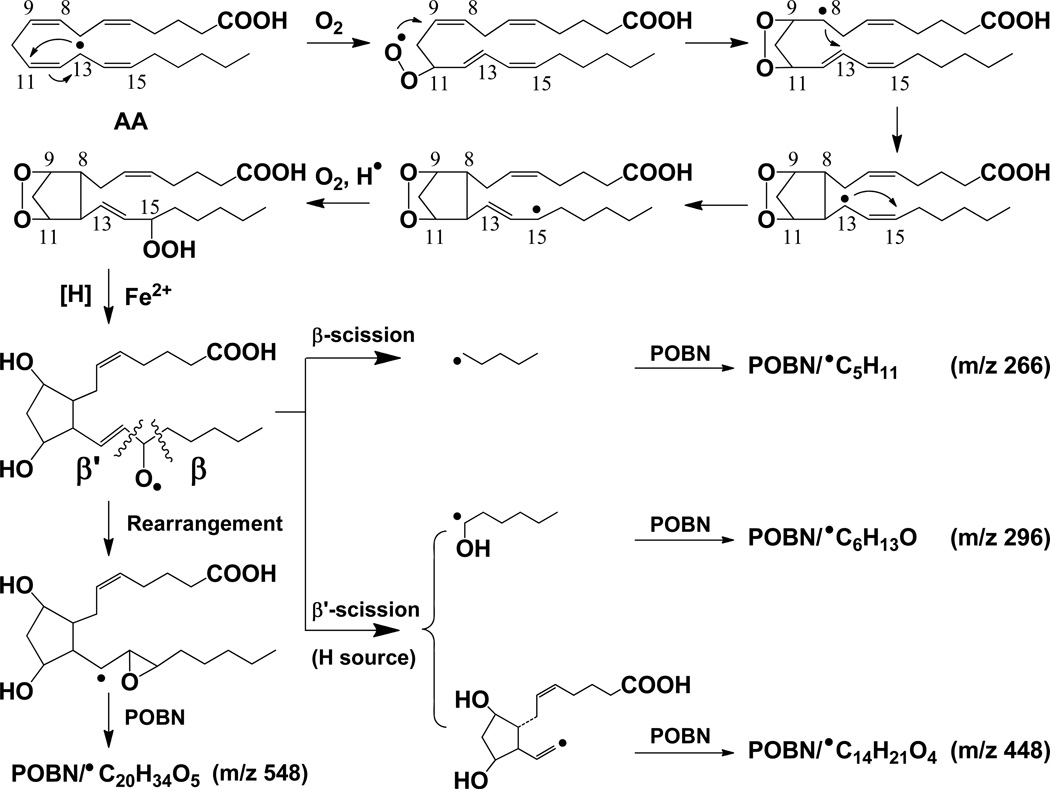
Scheme 1.
Proposed mechanism of COX-catalyzed AA peroxidation formation of free radicals via C-15 oxygenation [29]. Free radical reactions include the formation of C-13 radicals, C-9/C-11 endoperoxide bridge (adding the first O2 via the cyclooxygenase activity of COX), C-8 and C-12 cyclization, and C-15 oxygenation (adding the second O2 via the peroxidase activity of COX). Four types of free radicals, ●C5H11, ●C6H13O, ●C14H21O4 and ●C20H34O5, are listed as formed and trapped by POBN as m/z 266, m/z 296, m/z 448 and m/z 548 ions, respectively, in LC/MS. Note when β’-scission takes place at the PGF2 stage,1, 5 intra-molecular H abstraction results in formation of both ●C14H21O4 and ●C6H13O [29]. However, when β’-scission takes place at the PGH2 stage, ●C6H13O would be the only radical product as alternative cleavage pathway. Hexanol (a derivative of ●C6H13O) was detected in COX/AA systems by GC/MS (data not shown) from cellular experiments in which POBN was absent.