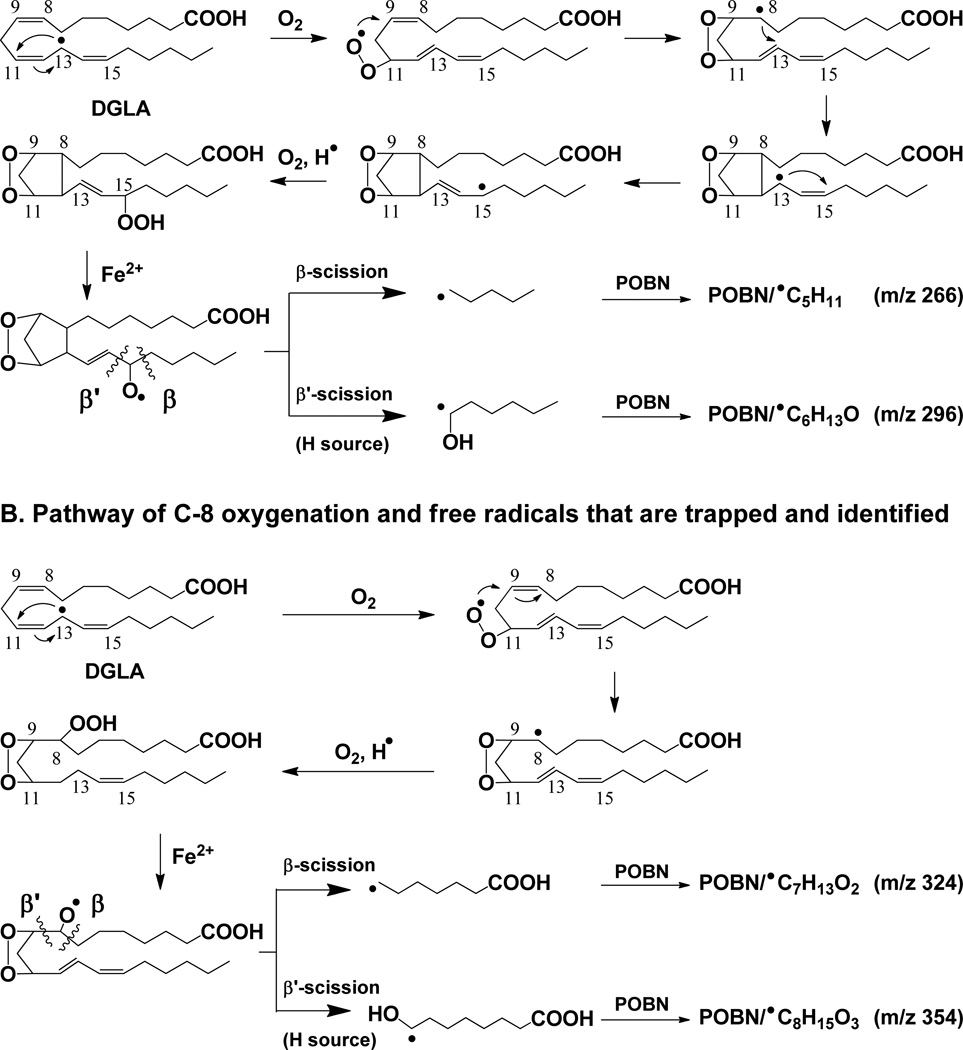
Scheme 2.
Proposed mechanism of COX-catalyzed DGLA peroxidation. (A) Formation of free radicals via C-15 oxygenation (same as described in Scheme 1, COX-catalyzed AA peroxidation). Thus, two radicals common to DGLA and AA peroxidation, ●C5H11 and ●C6H13O, were formed and trapped by POBN as m/z 266 and 296 ions, respectively, in LC/MS; and (B) Formation of free radicals via C-8 oxygenation, another way to add a second O2 onto DGLA followed by formation of the C-13 radical and C-9/C-11 endoperoxide bridge. Thus, two exclusive free radicals, ●C7H13O2 and ●C8H15O3, were formed and trapped by POBN as m/z 325 and m/z 355 ions, respectively, in LC/MS. Note that the β’-scission of a PGH1-type alkoxyl radical only forms ●C6H13O; no ●C=C radical forms from DGLA [32] as found in AA peroxidation. Hexanol (a derivative of ●C6H13O) was also detected in COX/DGLA systems by GC/MS (data not shown) from cellular experiments in which POBN was absent.