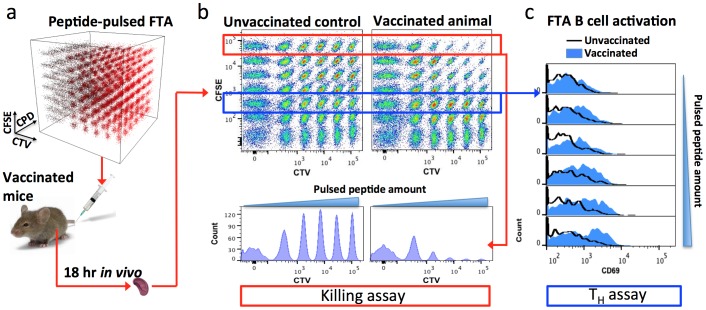
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a 252-parameter FTA assay.
Splenocytes from mice were labeled with combinations of CTV (0 nM, 350 nM, 1295 nM, 4792 nM, 17729 nM and 65595 nM), CFSE (0 nM, 79 nM, 315 nM, 1106 nM 3859nm, 13505nm and 47269 nM) and CPD (0 nM, 106 nM, 690 nM, 2738 nM, 10262 nM and 38506 nM) to generate 252 discernable cell clusters. Cell clusters were pulsed with MHC-binding peptides (as outlined in Figure 3) to generate a panel of 42 peptide pulsed clusters and this repeated 6 times to generate 6 intra-animal repeats (i.e., 252 target cell clusters in total). Target cells were also labeled with DiI for discrimination from host splenocytes (not shown). (a) FTA cells were injected i.v. into host mice that had 6 days earlier been vaccinated with VV-HIV or left unvaccinated as a control. 18 hr after FTA injection, splenocytes were collected and target cells delineated from host splenocytes by DiI label using flow cytometry (not shown). (b) 2D plots of the fluorescence intensities of a panel of one replicate of the 42 peptide-pulsed clusters from the unvaccinated and vaccinated animals and an associated histogram analysis of clusters pulsed with titrations of the F2L CTL epitope, revealing killing in vaccinated animals. (c) An example of histogram analysis of the FTA T helper assay, with B220+ FTA cells pulsed with the Gag Th TH cell epitope being assessed for CD69 up-regulation from the vaccinated animal compared to those from the unvaccinated animal.