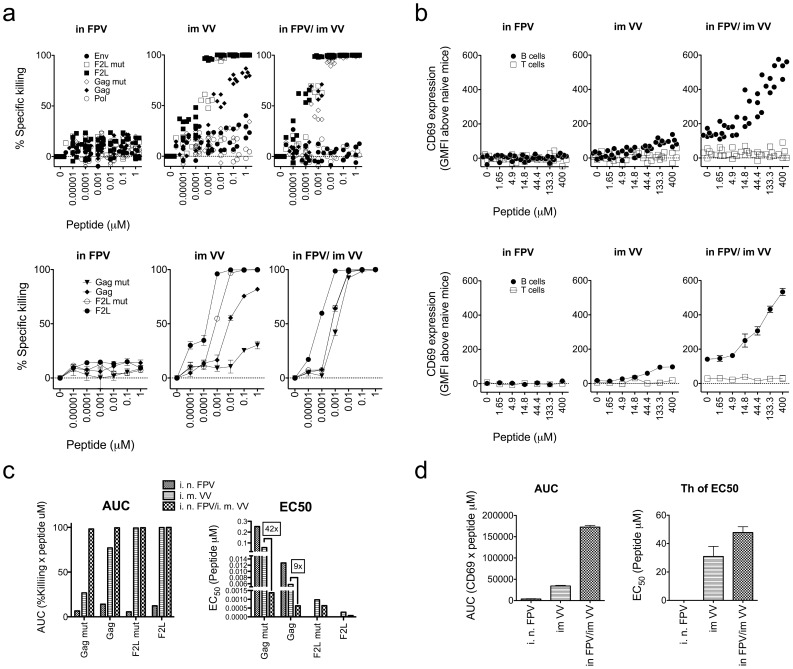
Figure 4. i.n.FPV-HIV/i.m.VV-HIV prime-boost vaccination improves the magnitude, functional avidity and epitope variant cross-reactivity of T-cell responses compared to prime or boost vaccinations alone.
Mice were vaccinated i.n. with FPV-HIV and/or i.m. VV-HIV. Mice were vaccinated with 5×106 PFU of each pox virus vaccine. Booster vaccinations were given 2 weeks post the previous vaccination. T-cell responses were assessed using 252-parameter FTAs as in Figure 3. a) % specific killing of FTA cells in vivo by CTL and b) TH cell activity induced by prime, boost, and prime-boost vaccination regimes, showing all 6 intra-animal replicate responses (upper panels) and means and standard error of means (lower panels) to the various CTL epitopes. b) Mean and standard error of means from a). AUC and EC50 values of: c) CTL responses and: d) TH cell responses. Values are only shown where EC50 values were calculable as described in the Methods. AUC and EC50 values are depicted as means from 5 intra-animal replicates. The results are representative of seven independent experiments.