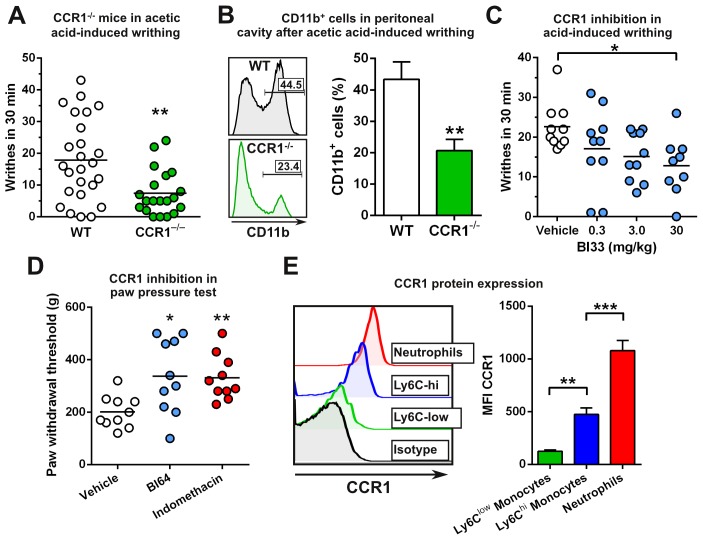
Figure 2. Knockout or inhibition of CCR1 decreases writhing which coincides with reduced myeloid cell recruitment.
(A) C57BL/6 WT and CCR1−/− mice were assessed in the acetic acid-induced writhing model. The number of writhes counted within 30 minutes is shown for each mouse (n = 12 for WT and 9 for CCR1−/−). (B) Peritoneal cells were assessed after the acetic acid-induced writhing test and the percentage of CD11b+ cells is shown (n = 5). (C) C57BL/6 mice were treated with BI33 or vehicle. After 30 min, mice were assessed in the acetic acid-induced writhing model (n = 9 or 10). (D) Han-Wistar rats were injected with CFA in the hind paw. Twenty-four hours later, rats were dosed with vehicle, BI64, or indomethacin at 30 mg/kg and assessed for mechanical hypersensitivity 2 hours later in the Randall-Selitto paw pressure test. The paw withdrawal threshold is shown in grams (n = 10). (E) CCR1 protein expression was assessed on blood CD11b+ cells (n = 6). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001.