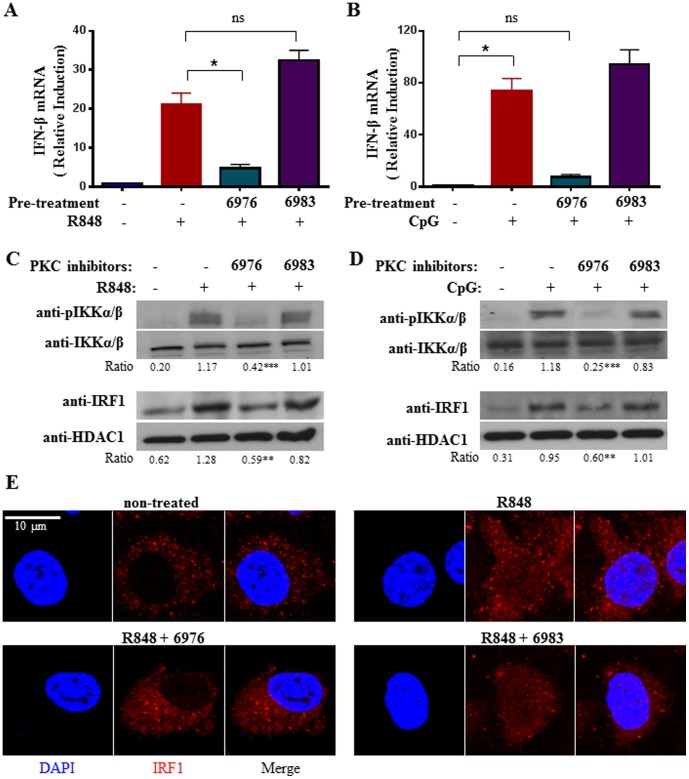
Figure 5. Chemical inhibition of PKCµ activity compromises TLR7/9-inducd IKKα/β and IRF-1 activation and IFN-β synthesis in cDC.
Wild type cDC were non-treated or pretreated for 30 mins with PKC inhibitors Gö 6976 (0.1 µM) or the non-inhibitory analog Gö 6983 (1 µM), followed by stimulation with R848 (1 µM) (A) or CpG (0.1 µM) (B) for 2 h and IFN-β mRNA expression was measured. Data were analyzed as in Fig. 2A. (C & D), Western blot analyses of IKKα/β and IRF-1 activation in PKCµ-inhibited TLR7/9-stimulated cDC. Wild type cDC were non-treated or pretreated for 30 mins with PKC inhibitors Gö 6976 (0.1 µM) or the non-inhibitory analog Gö 6983 (1 µM), followed by stimulation with R848 (1 µM) (C) or CpG (0.1 µM) (D) for 1 h. Activation of IKKα/β was examined using anti-phospho-IKKα (Ser180)/IKKβ (Ser181) antibody. The anti-IKKα/β blot served as loading control. Determination of IRF-1 activation was performed using anti-IRF-1 antibodies after nuclear extraction. The anti-HDAC1 immunoblots served as loading control. The ratios of the intensities of phospho-IKKα (Ser180)/IKKβ (Ser181) over IKKα/β and IRF-1 over HDAC1 are shown below the gels. **p<0.005, ***p<0.001 (Student's t test), compared to R848- or CpG-treated cells without PKCµ inhibition. (E) Confocal immunofluorescence study of IRF-1 localization in PKCµ-inhibited and R848-stimulated cDC. Wild type cDC were untreated or pre-treated for 30 mins with Gö 6976 (0.1 µM) or 6983 (1 µM), followed by stimulation with 1 µM R848 for 1 h. Bar = 10 µM. Results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.