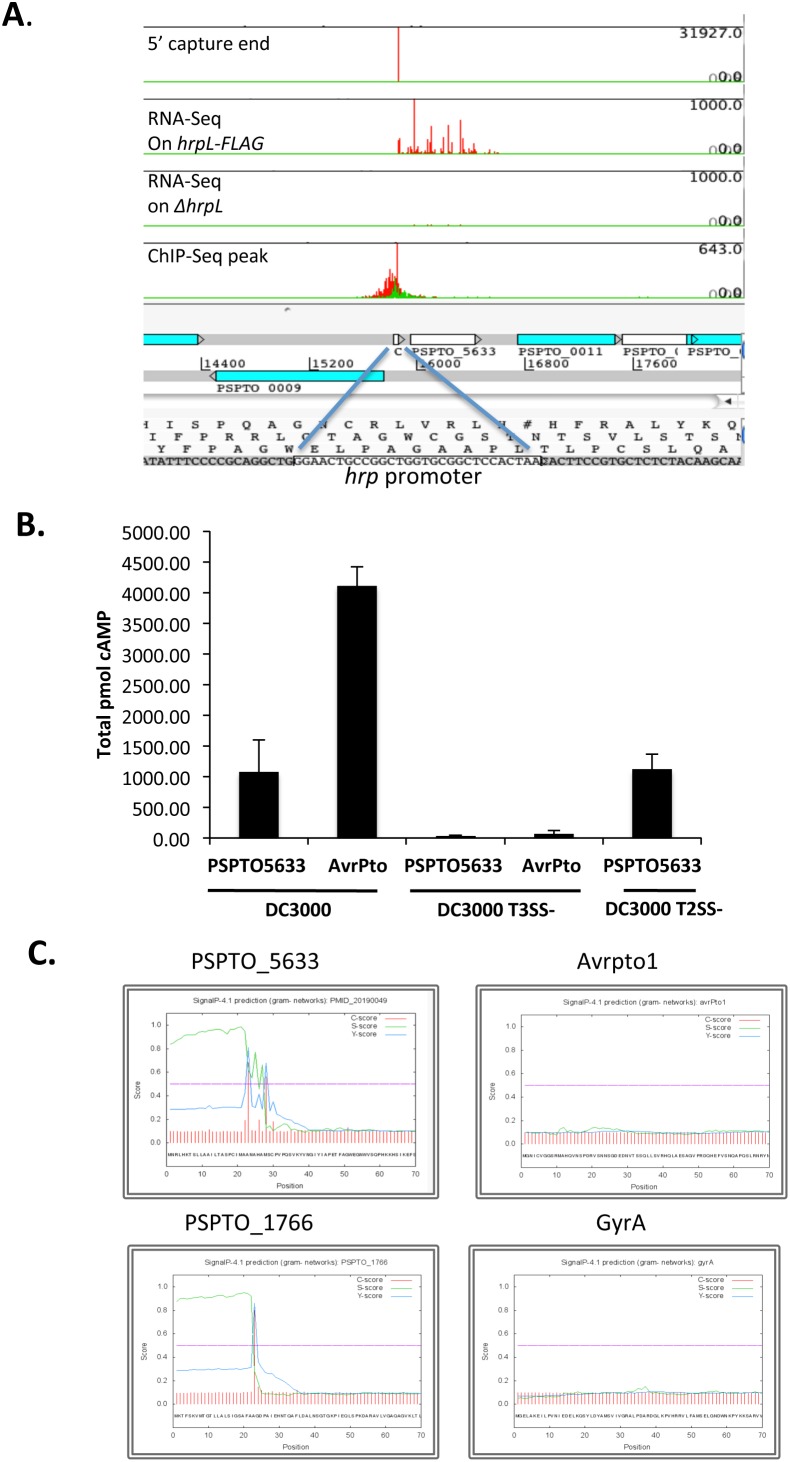
Figure 5. Summary of data for PSPTO_5633.
(A). ChIP-Seq, RNA-Seq and promoter motif at PSPTO_5633 locus. The transcription start site mapped by 5′ capture in RNA-Seq and its location relative to the predicted motif are consistent with the presence of a genuine hrp promoter. The profiles, along with genome annotation, are shown using Artemis. Red and green traces correspond to sequence read counts on the positive and negative strands, respectively. The sequence containing the hrp promoter motif is enclosed in a box. (B) Evidence that PSPTO_5633 is translocated through the DC3000 T3SS. N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with 5×107 CFU/ml of the indicated DC3000 strains carrying plasmids in which PSPTO_5633 was fused to the Cya translocation reporter, or an AvrPto-Cya control. Total cAMP produced as a result of Cya activity in leaf extracts 6 hours after infiltration is shown for all the strains. PSPTO_5633 is translocated into leaf cells from wild-type DC3000 (T3SS+) and from a DC3000ΔgspD (T2SS− mutant. No translocation was observed in the DC3000ΔhrcQ-U (T3SS− mutant) background. The data represent the average cAMP (pmol) with standard deviations computed using data from 3 plants. The experiment was repeated 3–5 times for all strains except for PSPTO_5633(DC3000 T2SS−), which was repeated twice. (C) SignalP analysis showing C, S and Y scores for each position in the sequence of PSPTO_5633, where C-score is the raw cleavage site score, S-score is the signal peptide score and Y-score is the combined cleavage site score. Similar analyses for avrPto1 (a T3SS-translocated effector), PSPTO_1766 (lipase, generally known to target the Sec pathway), and a housekeeping gene (gyrase, generally known to function inside bacterial cells) are shown for comparison.