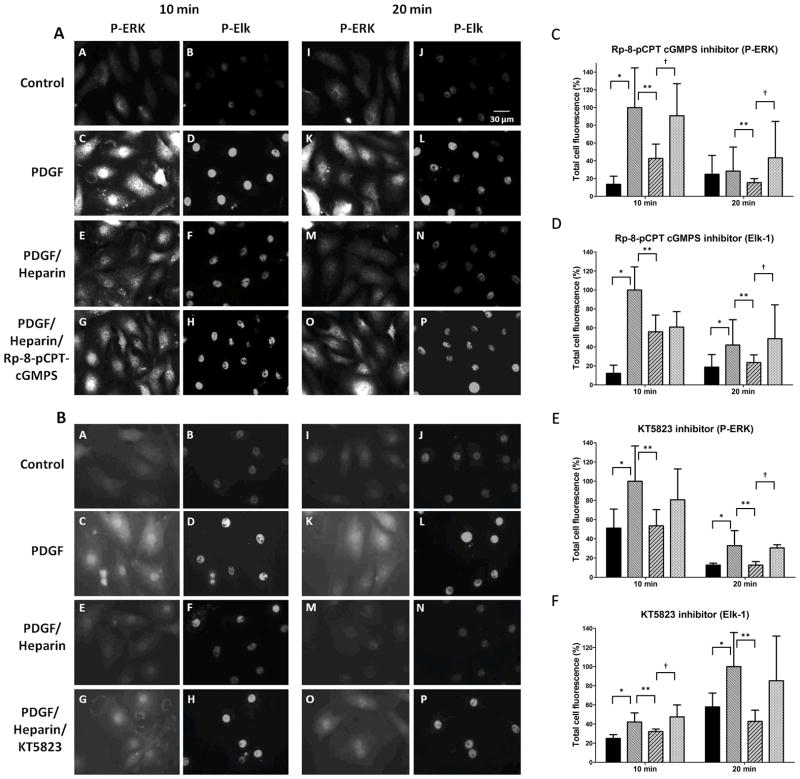
Figure 5.
PKG inhibitors interfere with heparin effects on ERK activation and Elk phosphorylation. A7r5 cells were cultured on cover slips as described in Methods, starved and treated with PDGF in the presence or absence of 200 μg/ml heparin. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, stained with primary antibodies against pERK (mouse) and pElk (rabbit) followed by FITC-labeled anti-mouse secondary antibodies and TRITC-labeled anti-rabbit secondary antibodies, and visualized as described in Methods. Some cells were treated with Rp-8-cCPT-cGMPS (panel A) or KT5823 (panel B) 10 min prior to heparin treatment. Pictures are representative of at least 3 experiments. Cells were analyzed using image J to determine intensity of pERK and pElk staining. Three experiments with 50 to 80 cells per experiment in each treatment were analyzed. For statistical analysis black bars represent untreated cells, medium intensity bars represent PDGF activated cells, diagonal striped bars represent heparin treated cells stimulated with PDGF, and the lightest bars represent cells treated with inhibitor prior to heparin and PDGF treatments. In all cases except for pERK staining at 20 min in panel C PDGF stimulation resulted in significant (p<0.05) increases in staining (*). Heparin-induced decreases in staining were significant (p<0.05) in all cases (**). Panel C data indicate pERK staining with Rp-8-cCPT-cGMPS which significantly reversed heparin effects (p<0.05) at both 10 and 20 min (†). Panel D data indicate pElk staining with Rp-8-cCPT-cGMPS which significantly reversed heparin effects (p<0.05) at 20 min (†). Panel E data indicate pERK staining with KT5823 which significantly reversed heparin effects (p<0.05) at 20 min (†). Panel F data indicate pElk staining with KT5823 which significantly reversed heparin effects (p<0.05) at 10 min (†).