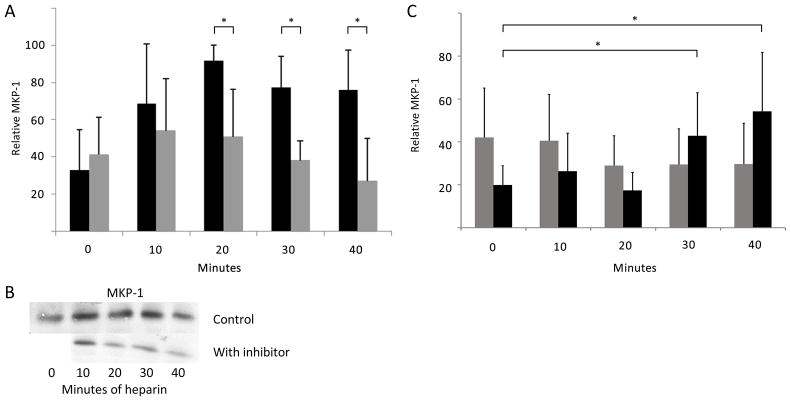
Figure 8.
Heparin-induced increases in MKP-1 require PKG activity. A. A7r5 cells were synchronized and left untreated or treated with 200 μg/ml heparin (dark bars). Identically treated cells were pre-treated with 2 μM Rp-8-pCPT-cGMS for 20 min prior to heparin (light bars) and cells were analyzed as described in Methods (n=7). MKP-1 expression was significantly different (*) between heparin and inhibited cells at 20, 30, and 40 min (p<0.05 in each case). B. One Western Blot experiment included in the data is illustrated. The blot was cut and aligned to show the same heparin points without inhibitor (above) and with inhibitor (below). No inhibitor without heparin was included in this blot. C. A7r5 cells were treated with siRNA to knock down PKG and treated with heparin as in A (light bars). For comparison, identical cells were treated with scrambled siRNA and then with heparin (dark bars). Cells were stained for PKG and MKP-1. Cells were analyzed using image J to determine intensity of MKP-1 staining. In knock down samples, cells were not analyzed if they stained strongly for PKG. Two experiments with more than 100 cells each were analyzed. In scrambled siRNA treated cells there were significant (*) increases in MKP-1 expression at 30 and 40 min (p<0.005). There were no increases in cells where PKG siRNA was used.