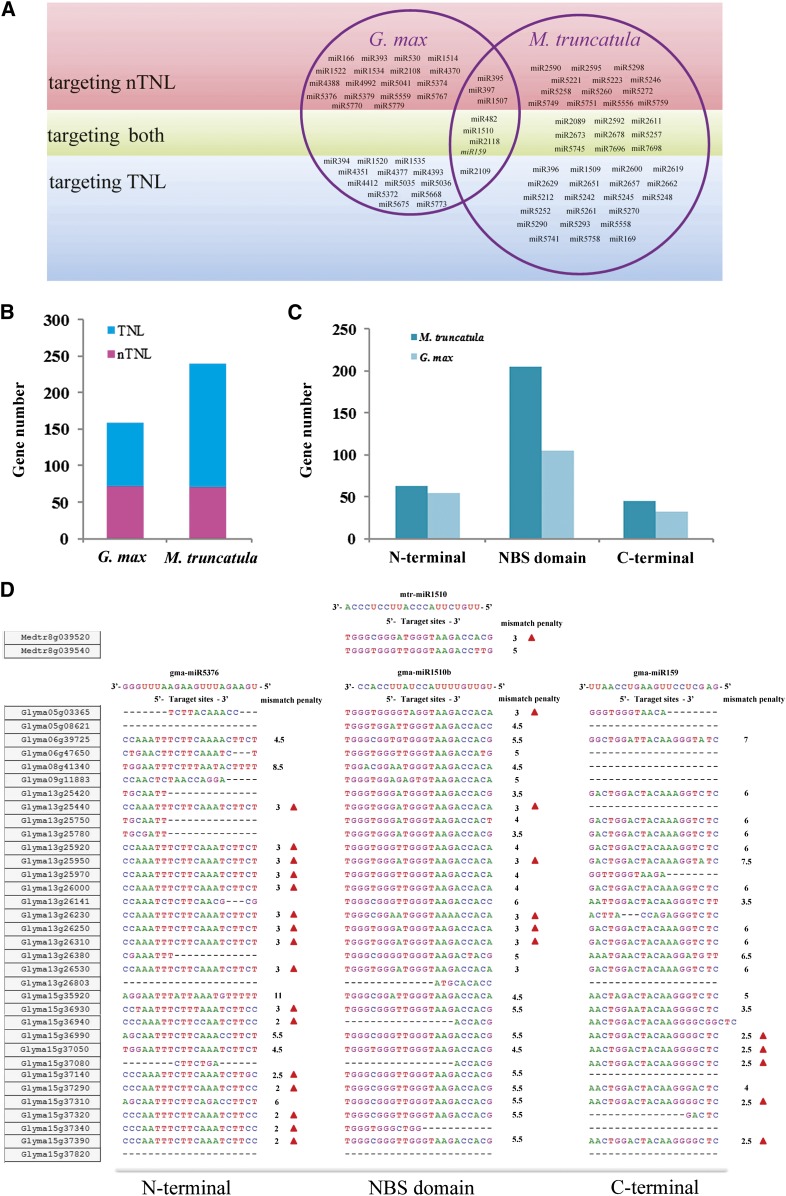
Figure 9.
Predicted regulation of microRNAs on NBS genes in M. truncatula and soybean. A, Summary of microRNA families predicted to target NBS genes in M. truncatula and soybean. The prediction process was performed by using the psRNATarget server with default settings, in which both the mismatch penalty (expectation value) and target accessibility (allowed maximum energy to unpair the target site) were taken into consideration. B, Numbers of TNL and nTNL subclass NBS genes that were predicted to be targeted by microRNAs in M. truncatula and soybean. C, Localization of microRNA target sites at different domains of NBS genes. D, An example showing the predicted NBS gene regulation pattern within nTNL-legume family 45 by three major microRNAs (miR5376, miR1510, and miR159). Certain NBS gene members were predicted to be regulated by the three microRNAs (shown with red triangles), and they all meet two conditions: the calculated mismatch penalty (expectation value) is no more than 3, and the estimated target accessibility value does not exceed 25 kcal mol−1. Nucleotide mutations, insertions, and deletions at the potential targeting sites often could be detected on genes that were not predicted to be targeted by a given microRNA. All missing nucleotides are indicated with dashes.