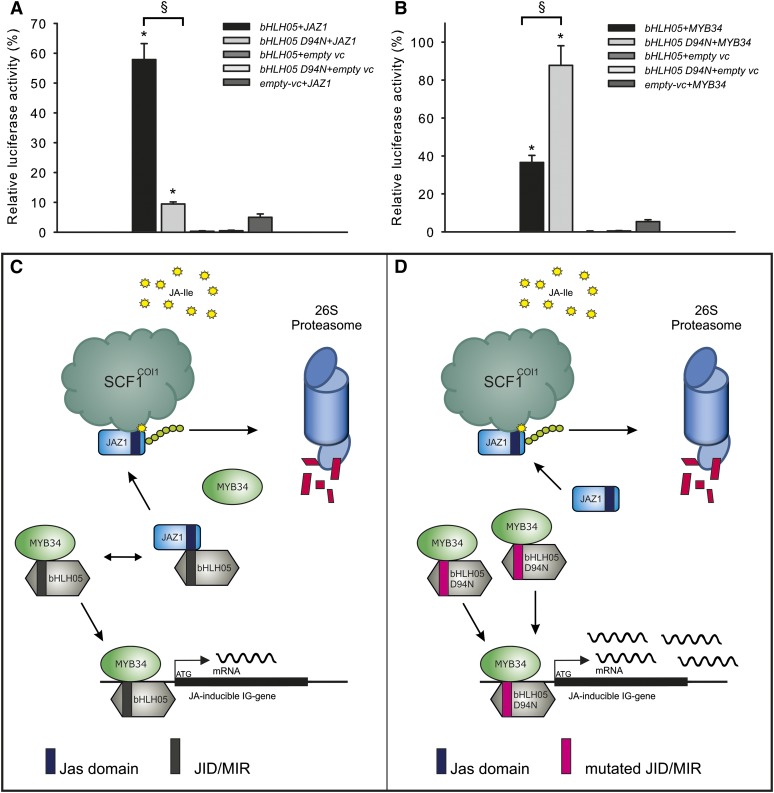
Figure 6.
Mutation D94N in the N-terminal part of bHLH05 prevents interaction of bHLH05 with JAZ1 and stimulates interaction with MYB34. A and B, LUMIER assays for the interaction of native bHLH05 and the mutated bHLH D94N (Asn at position 94) proteins with JAZ1 (A) and MYB34 (B) are shown. Interaction between luciferase-tagged MYB34 and JAZ1 on one side and the protein A-tagged bHLH05 and bHLH05 D94N on the other side are shown. The proteins were coexpressed in human cells (HEK293TN) and coimmunoprecipitated with IgG Dynabeads. Values marked with asterisks are significantly different from both empty vector controls (empty vc) without coding sequence fusion (Student’s t test; P < 0.05). Bars marked with § are significantly different from each other (Student’s t test; P < 0.001). C and D, Model for protein-protein interactions of native bHLH05 protein (C) and mutated bHLH05D94N protein (D) with MYB34 and JAZ1 proteins (without JA addition). C, The interaction of native bHLH05 with JAZ1 and MYB34 is balanced and bHLH05 interacts with both proteins, allowing production of IG only at basal (wild-type) levels. D, The mutation bHLH05D94N impairs the interaction with JAZ1 and triggers the strong interaction of bHLH05D94N with MYB34 followed by enhanced transcription of IG pathway genes and an increased accumulation of IG levels. The JAZ1 protein interacts less with bHLH05D94N and is therefore free for ubiquitinylation by CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 (COI1) and degradation by the 26S proteasome. The D94N mutation of bHLH05 mimics the presence of JA. Jas domain, The interaction domain of JAZ proteins used during the physical interaction with bHLH proteins; JID/MIR, a JAZ Interaction Domain/MYB Interaction Domain (a part of bHLH proteins, which allows the physical interaction with JAZ and MYB proteins).