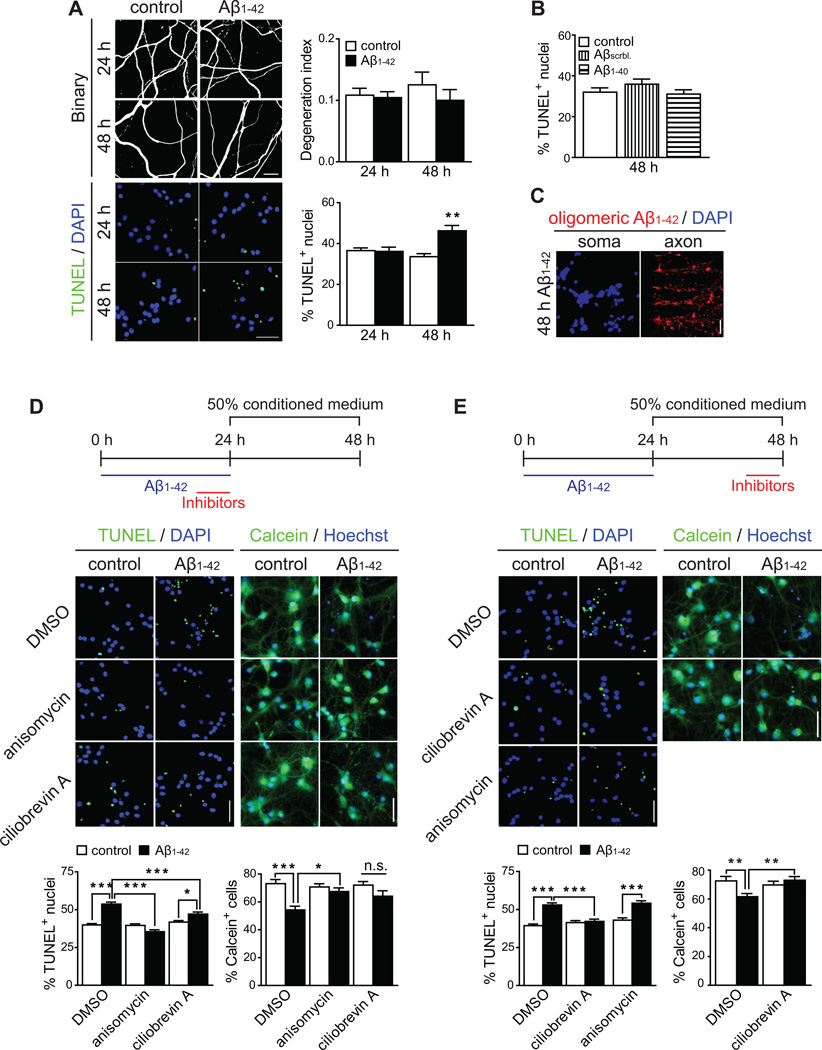
Figure 2. Intra-axonal protein synthesis and retrograde transport are sequentially required for Aβ1–42-induced somatic degeneration.
(A) Axons were treated with vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 24 or 48 h. Fragmentation of axonal tubulin (upper micrographs) or nuclear TUNEL staining (lower micrographs) were measured. Mean ±SEM of 25–55 axonal fields per condition (upper graph, n=5–11 biological replicates per group) and 50–70 somatic fields per condition (lower graph, n=5–7 biological replicates per group). **p<0.01.
(B) Axons were treated with vehicle, Aβscrambled or Aβ1–40 for 48 h. TUNEL-positive nuclei were quantified. Mean ±SEM of 25–35 optical fields per condition (n=5–7 biological replicates).
(C) Immunostaining for Aβ1–42 on axons and cell bodies.
(D) Inhibitors were applied to axons during the last 6 h of the 24 h Aβ1–42 treatment period. The culture medium from the axonal compartments was then replaced with 50% conditioned medium and cells were allowed to recover. Cell death (left panels) or survival (right panels), were assessed by TUNEL and Calcein staining, respectively. Mean ±SEM of 50–70 somatic fields stained for TUNEL per condition (left graph) and 25–31 somatic fields stained for Calcein (right graphs) per condition (n=5–7 biological replicates per group). *p<0.05; ***p<0.001.
(E) Inhibitors were applied to axons during the last 6 h of the 48 h experimental period. Cell death and survival were assessed as before. Mean ±SEM of 50–100 somatic fields stained for TUNEL per condition (left graph) and 30 somatic fields stained for Calcein (right graphs) (n=5–10 biological replicates). *p<0.05; ***p<0.001.
Scale bars, 50 µm. See also Figure S2.