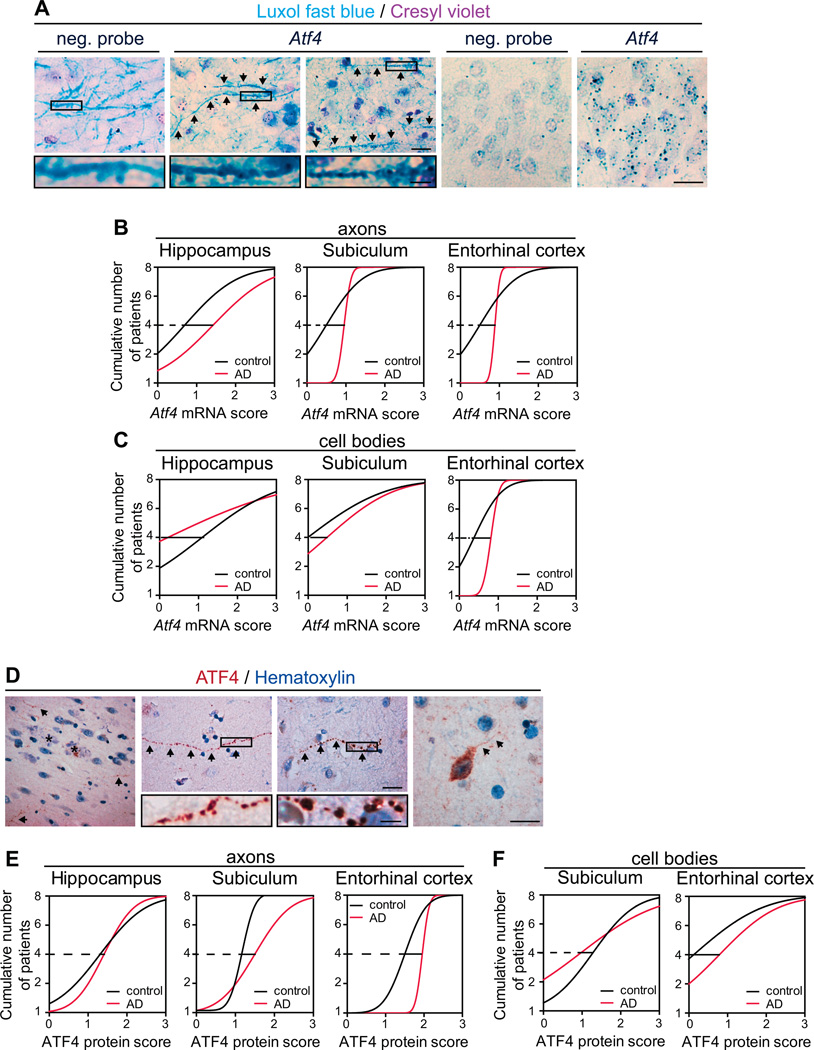
Figure 7. Presence of Atf4 mRNA granules and ATF4 protein in axons and axonal-like structures in the AD brain.
(A) Representative micrographs of Atf4 mRNA granules in axons and cell bodies in human brain samples. Panels 1–3: axons stained with luxol fast blue and a negative probe or an Atf4-targeting probe. Atf4-containing axons are indicated with arrows. Panels 4–5: examples of granule cells stained with cresyl violet and a negative or Atf4-targeting probe. Scale bars, 20 µm (Insets, 5 µm).
(B) Cumulative frequency distributions of Atf4-containing axons in the hippocampus, the subiculum, and the entorhinal cortex of control and AD cases (n=8 brains per condition).
(C) Cumulative frequency distributions of Atf4-containing cell bodies in the hippocampus, the subiculum, and the entorhinal cortex of control and AD cases (n=8 brains per condition).
(D) Representative micrographs of ATF4 protein in processes and cell bodies in human brain samples. First panel: an ATF4-positive process (arrows) in the vicinity of amyloid plaques (asterisks). Second panel: a relatively intact ATF4-positive process. Third panel: a beaded process. Fourth panel: A positive cell body and neurite (arrows). Scale bars, 20 µm (insets, 5 µm).
(E) Cumulative frequency distributions of ATF4-positive processes axons in the hippocampus, the subiculum, and the entorhinal cortex of control and AD cases (n=8 brains per condition).
(F) Cumulative frequency distributions of ATF4-positive cell bodies in the subiculum and the entorhinal cortex of control and AD cases (n=8 brains per condition).