Figure 1.
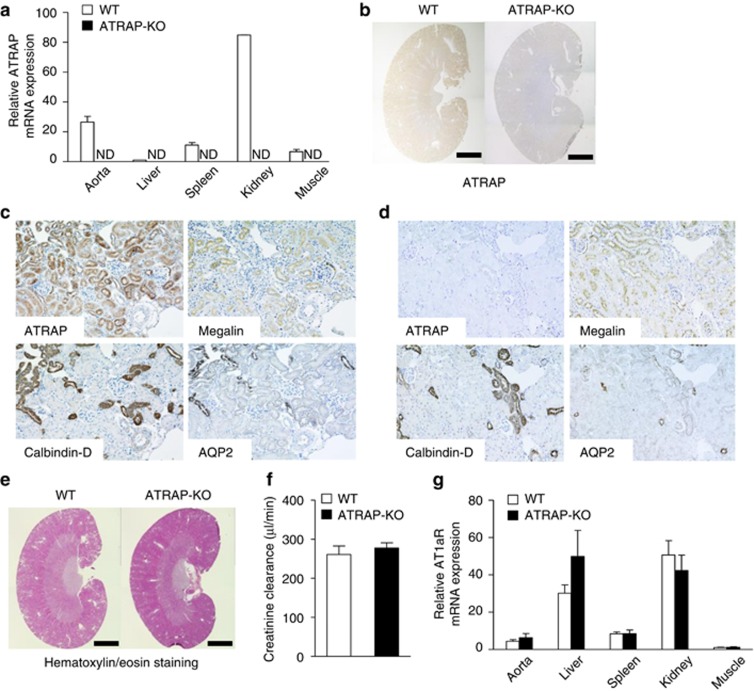
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)–associated protein (ATRAP) deficiency exerts no evident effect on renal morphology or AT1R gene expression. (a) ATRAP mRNA is widely distributed in many different tissues and abundantly expressed in the kidney of wild-type (WT) mice. Values are calculated relative to those achieved with extracts from the liver of WT mice and are expressed as mean±s.e. (n=2 in each group). ND, not detected. (b) ATRAP protein is abundantly expressed in the kidney of WT mice on immunohistochemistry. The positive areas for ATRAP immunostaining are evident as brown dots in the sections. Scale bar=1.5 mm. Original magnification × 40. (c) In WT mice, the ATRAP protein is expressed along the nephron segments from the proximal to distal tubules in consecutive renal cortical sections, as shown by immunohistochemistry. AQP2, aquaporin-2, a specific marker of the collecting ducts; Calbindin-D, a specific marker of distal convoluted tubules (DCTs) and connecting tubules (CNTs); Megalin, a specific marker of the proximal tubules. Original magnification × 200. (d) In ATRAP-knockout (KO) mice, there is no ATRAP immunostaining in the renal tubules. Original magnification × 200. (e) There is no anatomical difference between the kidneys of the WT and ATRAP-KO mice on representative hematoxylin/eosin staining of kidney sections. Scale bar=1.5 mm. Original magnification × 40. (f) ATRAP deficiency does not affect the creatinine clearance. Values are expressed as mean±s.e. (n=4 in each group). (g) ATRAP deficiency does not affect the tissue distribution or expression levels of AT1R mRNA. The values were calculated relative to those achieved with extracts from the muscles of WT mice and are expressed as mean±s.e. (n=4–6 in each group).