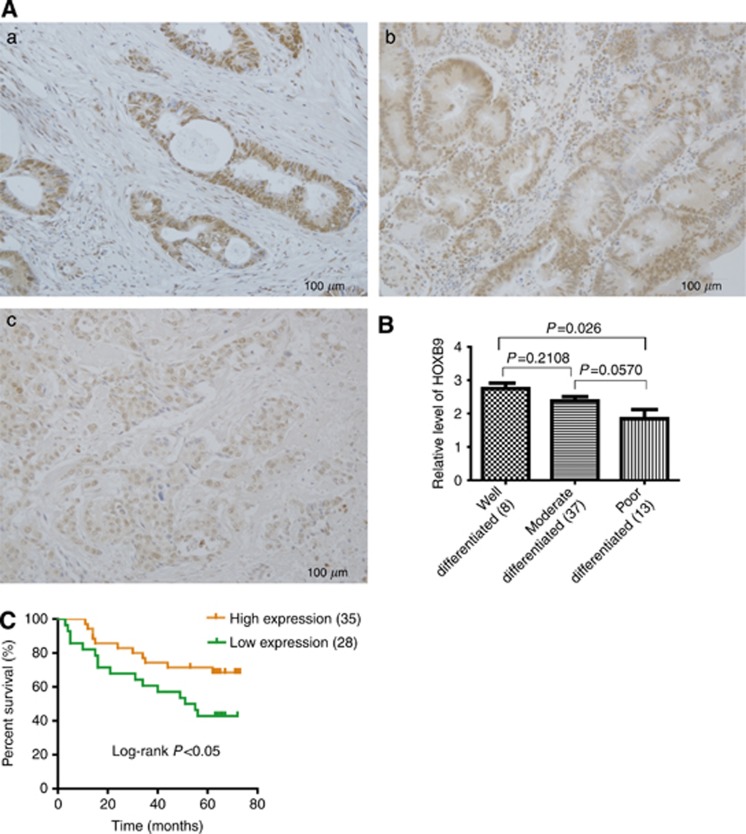
Figure 2.
Elevated expression of HOXB9 predicts longer overall survival for patients with colon adenocarcinoma. (A) HOXB9 differentially expressed in colon adenocarcinoma patients with different degree of differentiation. For patient samples: (a) well differentiated; (b) moderate differentiated; (c) poorly differentiated. (B) Semi-quantitative analysis of HOXB9 levels in colon adenocarcinoma patients with different degree of differentiation, in which HOXB9 expressed higher in well-differentiated adenocarcinoma than the moderate- or poorly differentiated ones. Statistical analysis was performed and the difference between well- and poorly differentiated is significant (P=0.026), whereas the differences between well- and moderate-differentiated tumours as well as moderate- and poorly differentiated tumours were not significant (Figure 2B, P=0.2108 and 0.0570 separately). (C) Two groups of colon adenocarcinoma patients with HOXB9 high or low expression were determined by Kaplan–Meier analysis with a log-rank at P<0.05, showing that elevated expression of HOXB9 correlates to a better overall survival for colon adenocarcinoma patients.