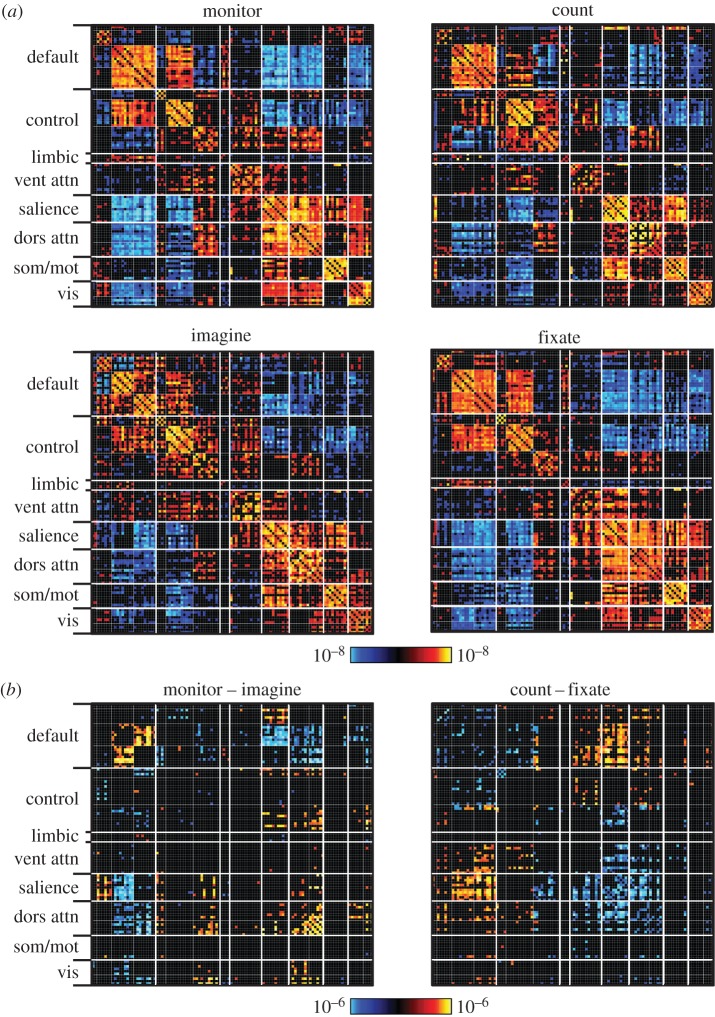
Figure 1.
Functional coupling within and between functional networks reveals similarities and differences across task states. Regions of interest obtained from the 17-network parcellation in Yeo et al. [12] were arranged by network membership. Correlation matrices were computed for four passive, continuous tasks collected in 48 subjects. Tasks were perceptually matched across conditions and required no overt responses. Tasks consisted of an external attention task (monitor), a backwards counting task (count), an episodic imagining task (imagine) and a passive fixation task (fixate). (a) Across all tasks, positive correlations predominantly fall along the diagonal, indicating that the arrangement according to network captures much of the structure of the coupling patterns in each task. (b) Examples of direct comparisons between task variants reveal differences in coupling within (along diagonal) and between (off-diagonal) functional networks.