Fig. 4. Nucleotide binding by V. vulnificus GspE•cyto-GspL and by V. cholerae GspE.
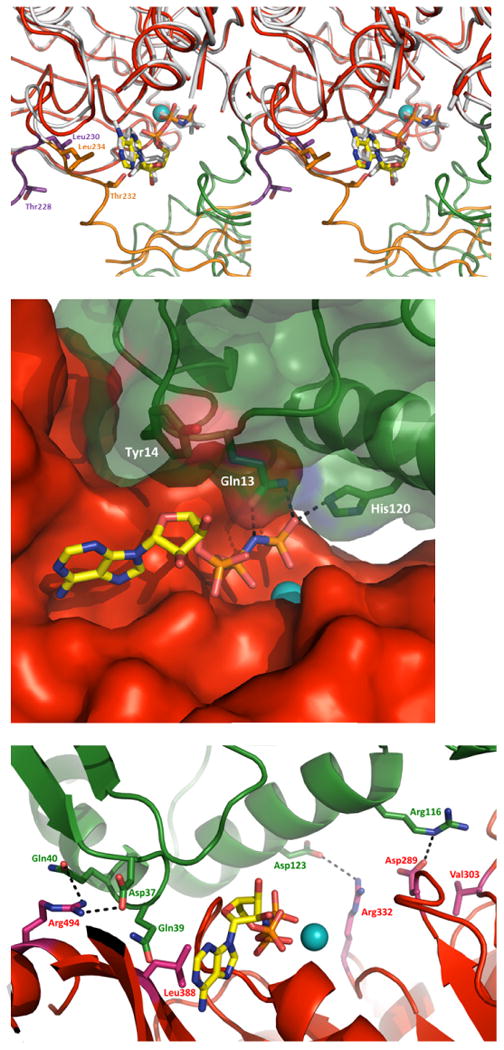
A. Superposition of V. vulnificus and V. cholerae GspE with AMPPNP bound (stereo figure). Residues that interact with AMPPNP in the V. cholerae GspE•AMPPNP complex but do not interact with AMPPNP in the V. vulnificus GspE•cyto-GspL•AMPPNP, due to a major change in conformation of the N2E-CTE linker (225-238), are shown in sticks. V. vulnificus: CTE red, N2E-CTE linker purple, cyto-GspL green, AMPPNP as sticks with yellow carbons, and Mg in cyan. V. cholerae: N2E and N2E-CTE linker orange, CTE white, and AMPPNP as white sticks (PDB 1P9W). Some CTE residues are removed for clarity.
B. V. vulnificus cyto-GspL•AMPPNPinteractions. Cyto-GspL residues Gln13 and His120 interact with the PNP of AMPPNP. Specifically, the side chains of Gln13 and His120 form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atoms of γ phosphorous atom with distances of ∼2.5-2.8 Å. The side-chain oxygen of Gln13 forms a hydrogen bond with a distance of ∼2.7 Å with the nitrogen linking the β and γ phosphor atoms. Tyr14 makes hydrophobic contacts with the ribose of AMPPNP.
C. Interactions between V. vulnificus Cyto-GspL and CTE. Key residues contributing to the cyto-GspL and CTE interactions are shown in sticks. The three Arg-Asp salt bridges are indicated with dashed lines. Residues making hydrogen bonds with main chain atoms of another subunit are also labeled.
