Figure 3.
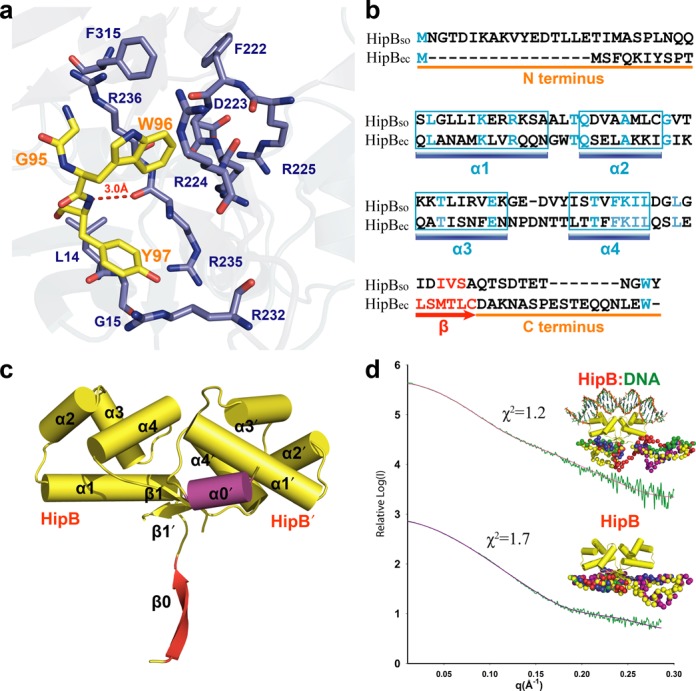
The flexible C-terminal tail of HipBso is accommodated by a hydrophobic pocket in HipAso. (a) Structural detail of the interaction site between HipBso (yellow) and HipAso (blue). (b) Structure-based sequence alignment of S. oneidensis and E. coli HipB (18% identity) showing the conserved W96 residue. (c) Crystal structure (2.35 A) of the HipBso dimer showing the different conformations of the N-termini forming a α0′ helix and β0 sheet, respectively. (d) SAXS modeling showing both HipBso and HipBso:DNA complex have a disordered N- and C-terminus. Five CORAL models, aligned with the N- and C-termini, are colored differently and shown in sphere representation.
