Figure 5.
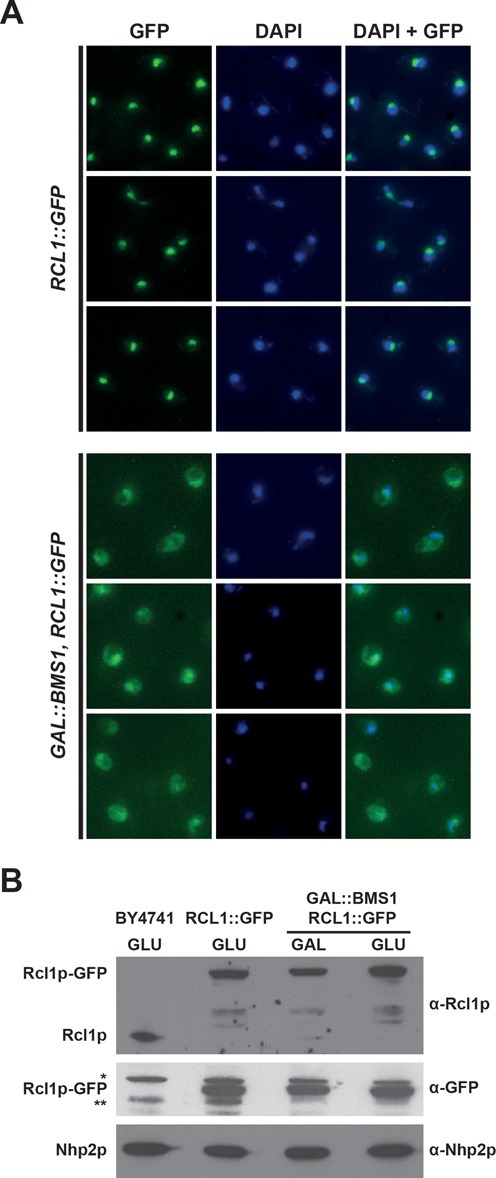
Bms1p depletion results in cytoplasmic accumulation of Rcl1p in yeast cells. (A) Subcellular localization of Rcl1p-GFP in the presence or absence of Bms1p. Upper 3 rows: yeast cells expressing a chromosomal GFP-tagged version of Rcl1p were grown in a glucose-containing rich medium. Lower 3 rows: yeast cells expressing Rcl1p-GFP and harbouring a chromosomal GAL1::BMS1 construct were shifted from a galactose- to a glucose-containing medium and grown for 11 h. In both cases, cells were harvested and processed for fluorescence microscopy. From left to right: Rcl1p-GFP fluorescence signal (green), DAPI staining (blue), merged images. (B) Accumulation levels of Rcl1p-GFP in the presence or absence of Bms1p. Yeast cells expressing Rcl1p-GFP and harbouring the chromosomal GAL1::BMS1 construct were shifted from a galactose- to a glucose-containing medium and grown for 11 h. Cells were harvested, total proteins were extracted and analysed by western blot using the indicated antibodies. The RCL1::GFP and BY4741 strains were grown on a glucose-containing medium and processed in parallel to determine the accumulation levels of Rcl1p-GFP and the endogenous Rcl1p protein, respectively, in these conditions. The nucleolar protein Nhp2p was detected as a loading control. * and **, non-specific proteins detected with the anti-GFP antibodies.
