Figure 7.
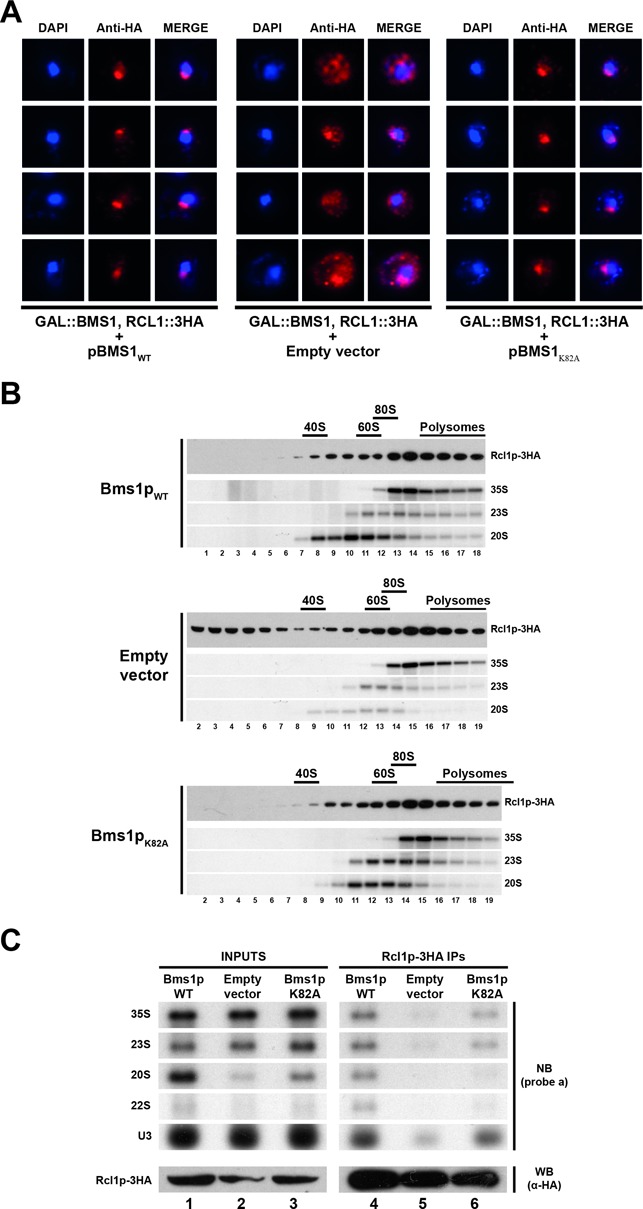
GTP binding to Bms1p is not required for incorporation of Rcl1p into pre-ribosomes. (A) Subcellular localization of Rcl1p-3HA in cells expressing Bms1pK82A or in ‘wild-type’ or Bms1p-depleted cells as controls. A yeast strain expressing Rcl1p-3HA and harbouring the chromosomal GAL::BMS1 construct was transformed with vectors expressing wild-type Bms1p (left panel), Bms1pK82A (right panel) or with the empty vector as a control (central panel). The resulting strains were shifted from a galactose- to a glucose-containing medium and grown for 20 h. Cells were harvested and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-HA antibodies. From left to right: DAPI (4',6'-diamidino-2-phénylindole) staining (blue), Rcl1p-3HA immunofluorescence signal (red) and the merged images. (B) Sucrose gradient sedimentation profile of Rcl1p using extracts from cells expressing ‘wild-type’ Bms1p (upper panel), Bms1pK82A (lower panel) or from Bms1p-depleted cells (central panel). The yeast strains grown as described in panel A were treated with cycloheximide and harvested. Total extracts were prepared and sedimented through 4.5–45% sucrose gradients. Twenty fractions were collected from which RNAs and proteins were extracted. Rcl1p-3HA was detected in the protein samples by western blot using anti-HA antibodies. The 35S, 23S and 20S pre-rRNAs were detected by northern blot using probe ‘a’. (C) Pre-rRNAs associated with Rcl1p-3HA in cells expressing Bms1pK82A or in ‘wild-type’ or Bms1p-depleted cells as controls. The pre-ribosomal particles containing Rcl1p-3HA were immunoprecipitated from extracts corresponding to the different strains grown as described in (A). The associated RNAs were analysed by northern blot using probe ‘a’ and probe ‘U3’.
