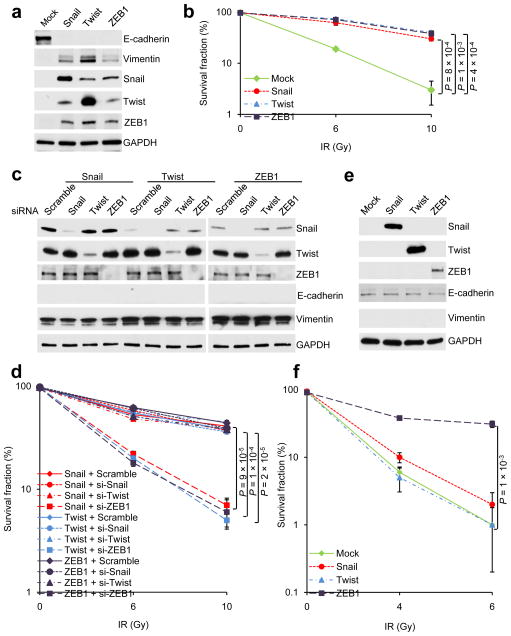
Figure 1. ZEB1 confers radioresistance on mammary epithelial cells.
(a) Immunoblotting of E-cadherin, Vimentin, Snail, Twist, ZEB1 and GAPDH in HMLE cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1.
(b) Clonogenic survival assays of HMLE cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1. n = 3 wells per group.
(c) Immunoblotting of Snail, Twist, ZEB1, E-cadherin, Vimentin and GAPDH in HMLE cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1 alone or in combination with the siRNA targeting Snail, Twist or ZEB1.
(d) Clonogenic survival assays of HMLE cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1 alone or in combination with the siRNA targeting Snail, Twist or ZEB1. n = 3 wells per group.
(e) Immunoblotting of Snail, Twist, ZEB1, E-cadherin, Vimentin and GAPDH in MCF7 cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1.
(f) Clonogenic survival assays of MCF7 cells transduced with Snail, Twist or ZEB1. n = 3 wells per group.
Data in b, d and f are the mean of biological replicates from a representative experiment, and error bars indicate s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. The experiments were repeated 3 times. The source data can be found in Supplementary Table 3. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 7.