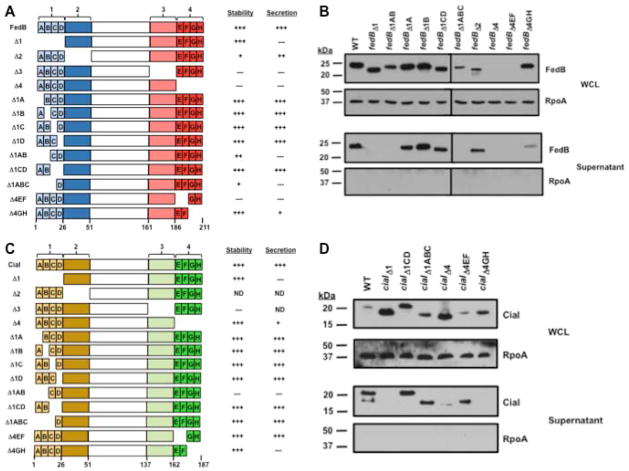
Figure 1. Identification of intramolecular domains of FedB and CiaI required for secretion.
(A) Domains and subdomains of C. jejuni FedB and a summary of their level of stability and secretion. The N- and C-terminal domains of FedB were divided into domains of 25 amino acids in length. FedB N-terminal domains are indicated in light blue (domain 1) or dark blue (domain 2). FedB C-terminal domains are indicated in pink (domain 3) or red (domain 4). Domains 1 and 4 were further divided into subdomains A–D or E–H, respectively, that were each six or seven amino acids in length. Each mutant protein that was constructed and analyzed is shown. A summary of the relative level of stability and secretion of mutant FedB proteins as assessed qualitatively by immunoblots are relative to WT FedB, which was set to “+++”. (B) Immunoblot analysis of WT and FedB mutant proteins in C. jejuni whole-cell lysates (WCL) and supernatants after growth in MH broth. WT and FedB mutant proteins were expressed from the native promoter in trans in C. jejuni 81-176 ΔfedB. All strains were grown in MH broth for 4 h at 37 °C in microaerobic conditions. WCL and supernatant proteins were recovered and analyzed by immunoblotting with antiserum specific for FedB or RpoA, which served as a control for a cytoplasmic protein. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa. (C) Domains and subdomains of C. jejuni CiaI and a summary of their level of stability and secretion. The N- and C-terminal domains of CiaI were divided into domains of 25 amino acids in length. CiaI N-terminal domains are indicated in light yellow (domain 1) or dark yellow (domain 2). CiaI C-terminal domains are indicated in light green (domain 3) or dark green (domain 4). Domains 1 and 4 were further divided into subdomains A–D or E–H, respectively, that were each six to seven amino acids in length. Each mutant protein that was constructed and analyzed is shown, except where indicated by “ND” (not determined). A summary of the relative level of stability and secretion of mutant CiaI proteins as assessed qualitatively by immunoblots are relative to WT CiaI, which was set to “+++”. (D) Immunoblot analysis of WT and CiaI mutant proteins in C. jejuni WCL and supernatants after growth in MH broth. WCL and supernatant proteins were recovered as described in (B) and analyzed by immunoblotting with antiserum specific for CiaI or RpoA, which served as a control for a cytoplasmic protein. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa