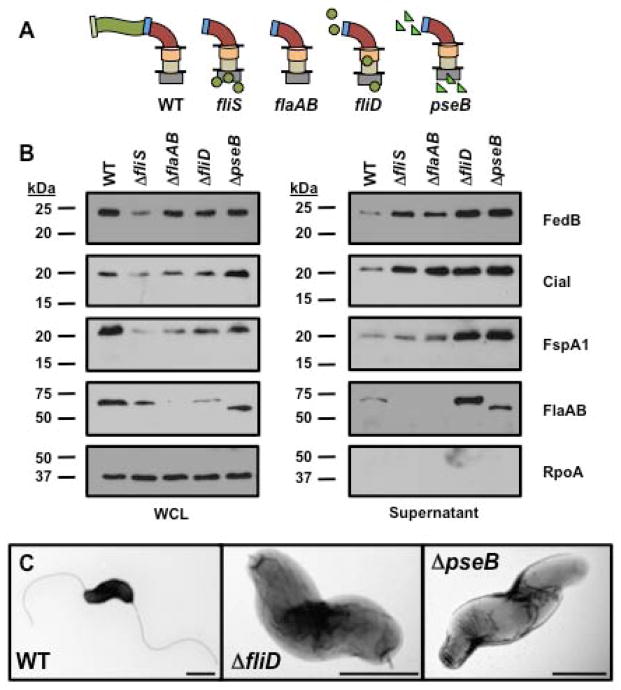
Figure 5. Secretion of flagellins, FedB, CiaI, and FspA1 in C. jejuni mutants defective in filament biosynthesis.
(A) Diagram of representative flagellar structures produced by specific C. jejuni flagellar mutants. General substructures of the flagellum include flagellar T3SS, MS ring and C ring (grey box), proximal rod (tan cylinder), distal rod composed by FlgG (orange cylinder), hook (red curve), hook-filament junction (blue rectangle), filament (green wave), FliD filament cap (light green rectangle), FlgD hook cap (pink rectangle), glycosylated flagellins (green circles), and unglycosylated flagellins (green triangles). Lines indicate inner and outer membranes. (B) Immunoblot analysis of FedB, CiaI, FspA1 and flagellar proteins in whole-cell lysates (WCL) or culture supernatants. WT and C. jejuni isogenic mutants lacking proteins required for filament biosynthesis were grown in MH broth for 4 h at 37 °C in microaerobic conditions. WCL and supernatant proteins were recovered and analyzed by immunoblotting with antisera specific for each protein or RpoA, which served as a control for a cytoplasmic protein. The antisera for flagellins recognized both FlaA and FlaB, which are of similar size. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa. (C) Electron micrographs of WT and isogenic C. jejuni filament synthesis mutants lacking fliD, encoding the filament cap, and pseB, encoding an enzyme required for O-linked glycosylation of flagellin. The bar represents 0.5 μm.