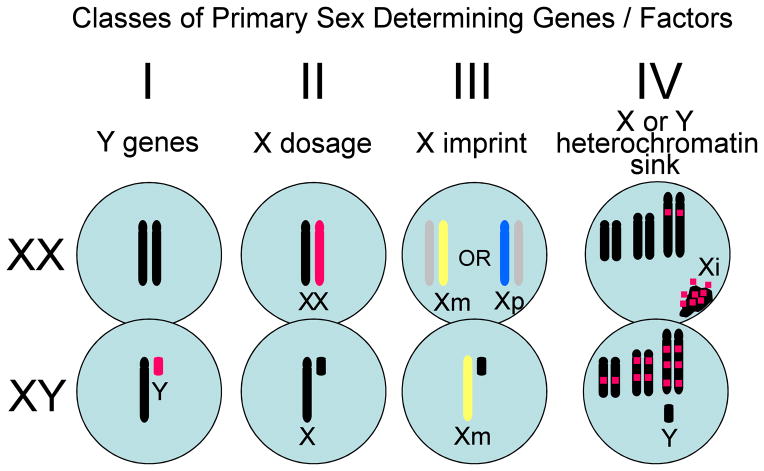
Figure 1.
Four classes of primary sex-determining factors that are encoded by the sex chromosomes. Class I are Y genes found only in males. Class II are X genes that escape inactivation and are inherently expressed higher in females than males. Class III are X genes that are imprinted and have a sex-biasing effect because of expression of the paternal imprint only in XX cells. Class IV are putatitve heterochromatic regions on the sex chromosomes (the X chromosome is illustrated here), which act as sinks to sequester heterochromatizing factors from other chromosomes and alter the epigenetic status of autosomes. Reprinted from Arnold, 2011, Trends in Genetics.