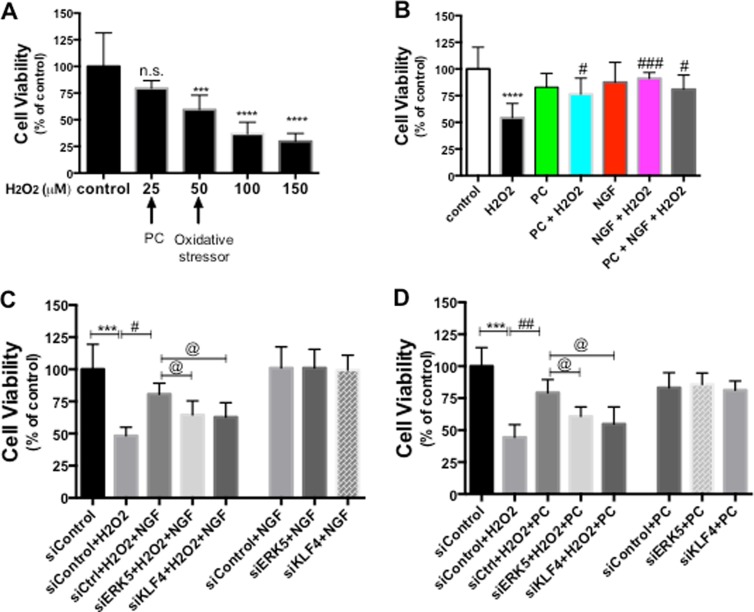
Fig. 9.
ERK5/KLF4 pathway is required for NGF- and PC-induced protection against oxidative stress in mouse primary hippocampal neurons. a Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2 for 24 h before cell viability was assessed by CalceinAM assay (n = 4). 25 μM H2O2 was chosen as the preconditioning concentration, while 50 μM H2O2 was used as the oxidative stressor in the following experiments. b Primary neurons were pre-treated with PC or NGF for 24 h prior to treatment with H2O2 (50 μM) for another 24 h, then cell viability was assessed (n = 3). Both PC and NGF rescued neurons from H2O2 (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control, respectively). # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 versus H2O2. c, d Primary neurons were transfected with siControl, siERK5 or siKLF4 for 24 h before NGF or PC was applied for another 24 h. Cells were then stressed with H2O2, and assessed for cell viability (n = 3). While NGF and PC both increased cell viability against H2O2 (# p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01), siERK5 or siKLF4 abolished this effect (@: p < 0.05 compared to siControl + H2O2 + NGF [or PC]). NGF or PC alone did not affect cell viability (ns between siControl + NGF [or PC] vs. siControl). Without H2O2 stress, siERK5 or siKLF4 did not affect the protective effect by NGF or PC (ns between siERK5 + NGF [or PC], siKLF4 + NGF [or PC] vs. siControl + NGF [or PC])