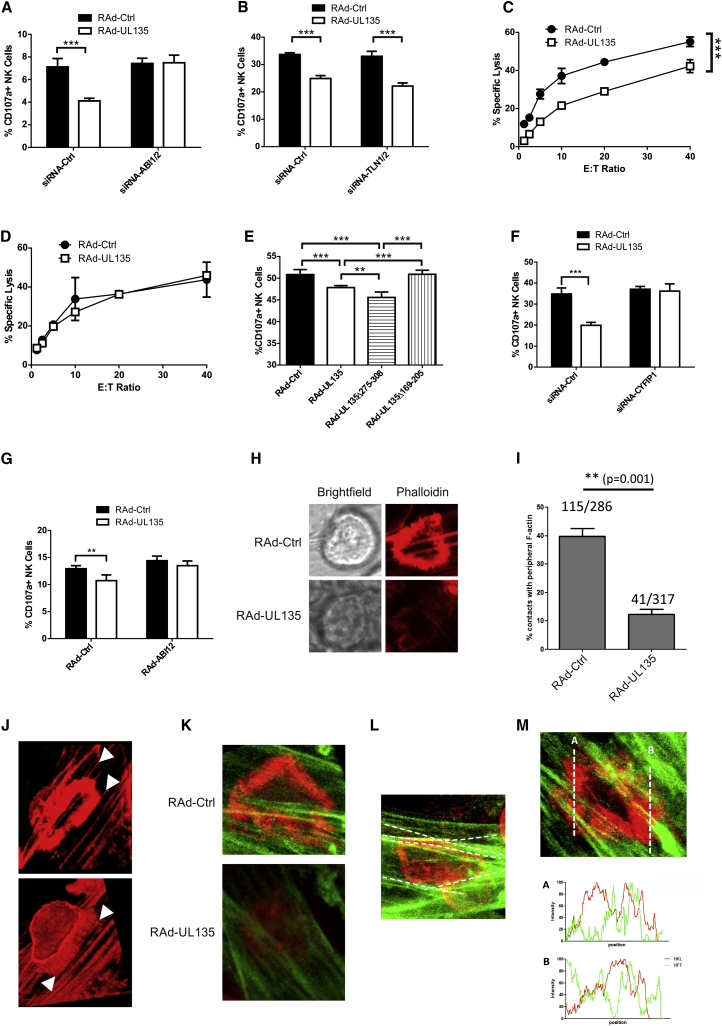
Figure 6.
Interactions with ABI1/ABI2 Are Required for UL135 to Protect Against NK Cells
(A and B) HFFF-hCAR were transfected with control siRNA (siRNA-Ctrl), siRNA against ABI1 and ABI2 (siRNA-ABI1/ABI2), or siRNA against talin-1 and talin-2 (siRNA-TLN1/2). They were infected 24 hr later with RAd-UL135 or RAd-Ctrl. NK degranulation assays were performed 48 hr postinfection with IFN-α-activated PBMC.
(C and D) Cytotoxicity assays were performed with IFN-α-activated T-cell-depleted PBMC against HFFF-hCAR transfected with siRNA-Ctrl (C) or siRNA-ABI1/ABI2 (D) and then infected with either RAd-Ctrl or RAd-UL135.
(E) HFFF-hCAR were infected with the indicated adenovirus vectors, and NK cell degranulation assays were performed 48 hr postinfection with IFN-α-activated PBMC.
(F) Cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against CYFIP1. They were infected 24 hr later with RAd-UL135 or RAd-Ctrl. NK degranulation assays were performed 48 hr postinfection with IFN-α-activated PBMC.
(G) HFFF-hCAR were infected with RAd expressing ABI1 and ABI2 (RAd-ABI1+ABI2), RAd-UL135, or empty control vector (RAd-Ctrl) in the combinations indicated, and NK cell degranulation assays were performed 48 hr postinfection with IFN-α-activated PBMC. Results of are means ± SD of quadruplicate samples. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(H and J) HFFF-hCAR were infected with RAd-Ctrl or RAd-UL135. NKL cells were added 48 hr postinfection, allowed to settle, and then fixed and stained with phalloidin. Images show the immune synapse between fibroblasts and NKL cells.
(I) Quantitation of NKL:HFFF interactions in (H).
(J) 3D reconstruction of the IS is shown in the top panel. Arrows indicate actin fibers in the target that define the inner or outer edge of the synapse.
(K and L) Fibroblasts expressing lifeact-Citrine were infected with RAd-Ctrl or RAd-UL135 and incubated with NKL-cell-expressing lifeact-mCherry 48 hr later.
(K) Differential imaging of F-actin within a fibroblast (green) and NKL cell (red) at the IS.
(L) Actin fibers in RAd-Ctrl infected fibroblast that align with the extent of actin polymerization in the NKL cell are highlighted in white.
(M) Intensity profiles of actin along the indicated regions of the IS within the fibroblast (green) or NKL cell (red).