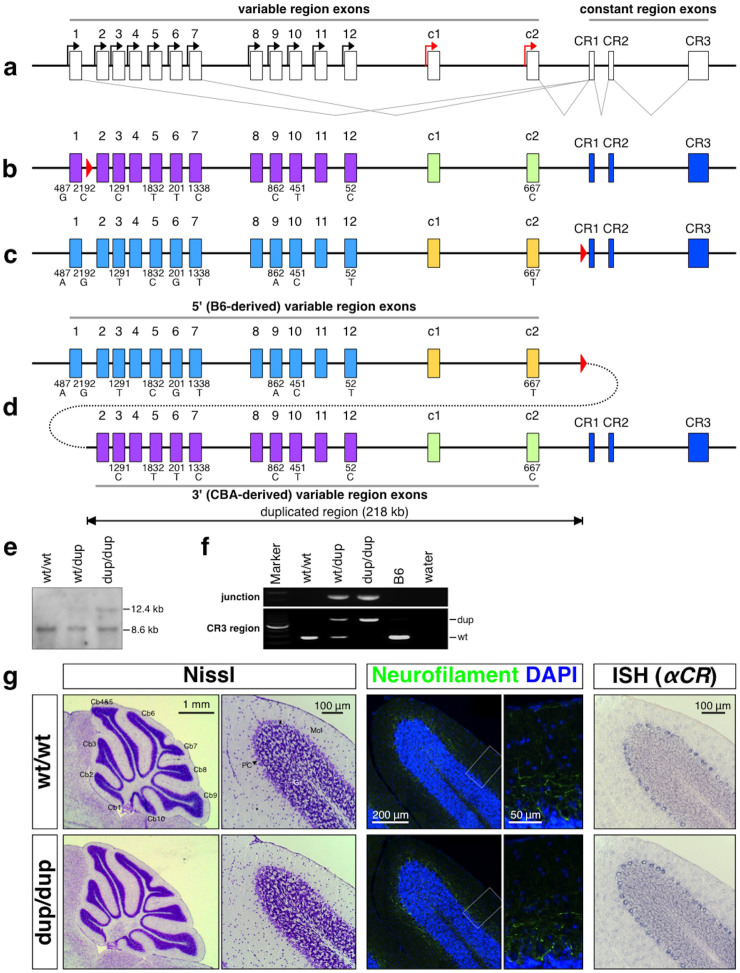
Figure 1. Targeted tandem duplication in the Pcdh-α cluster.
(a) Genomic structure of the Pcdh-α wild-type allele. The Pcdh-α allele consists of variable region exons (1–12, c1 and c2) and constant region exons (CR1–CR3). Each variable region exon is transcribed from its own promoter in a stochastic (black arrows) or constitutive (red arrows) manner. A Pcdh-α transcript is produced from one of the variable region exons and the set of constant region exons by splicing. (b) The G16Neo allele: a loxP site was inserted between Pcdh-α1 and Pcdh-α2. The loxP site is shown as a red triangle. (c) The SR allele: a loxP site was inserted between Pcdh-αc2 and CR1. (d) The dup(2-c2) allele: duplication of Pcdh-α2-Pcdh-αc2. The dup(2-c2) allele was produced by Cre-loxP-mediated trans-allelic meiotic recombination between the G16neo and SR alleles. The duplicated segments are shown under the position of the original segments. Importantly, each duplicate Pcdh-α3, Pcdh-α5, Pcdh-α6, Pcdh-α7, Pcdh-α9, Pcdh-α10, Pcdh-α12, and Pcdh-αc2 could be distinguished by SNP analysis; the 5′ genes were from B6 and the 3′ ones were from CBA. (e & f) Confirmation of the duplication allele by Southern blotting (e) and PCR (f). G, Histological analysis of the cerebellum of 4-week-old wild-type and Pcdhαdup(2-c2)/dup(2-c2) mice. Nissl staining (left), immunostaining for neurofilament (middle), and in situ hybridization using a Pcdh-α CR probe (right). Cb1-10, 1st – 10th lobule of the cerebellum; Gra, granule cell layer; Mol, molecular layer; Pur, Purkinje cell layer.