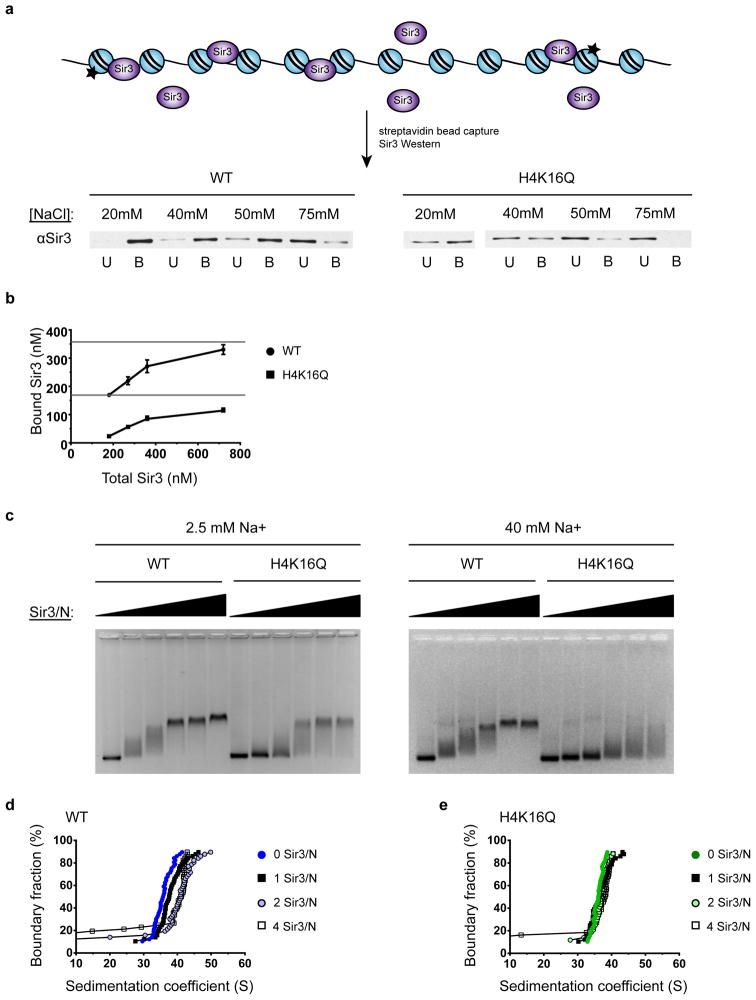
Figure 1. Increased ionic strength buffer enhances the nucleosome-specific binding of Sir3.
(a) Nucleosomal array capture and Western blot analysis of Sir3 unbound (U) and bound (B) to WT and H4-K16Q arrays. (b) Quantification of bound vs. unbound Sir3 to WT and H4-K16Q arrays of an experiment performed as in (a) using increasing Sir3 concentrations in 40 mM NaCl. (c) EMSA of Sir3 binding to WT and H4-K16Q 12-mer arrays in Tris containing 2.5 mM NaCl buffer (left) and phosphate buffer at ~40 mM Na+ (right). Sir3/N is the number of Sir3 monomers per nucleosome positioning sequence, ranging from 0 to 8. (d,e) SV-AUC analyses. vHW plots of Sir3 binding to WT and H4-K16Q arrays, respectively. Sir3/N is the number of Sir3 monomers per nucleosome positioning sequence.