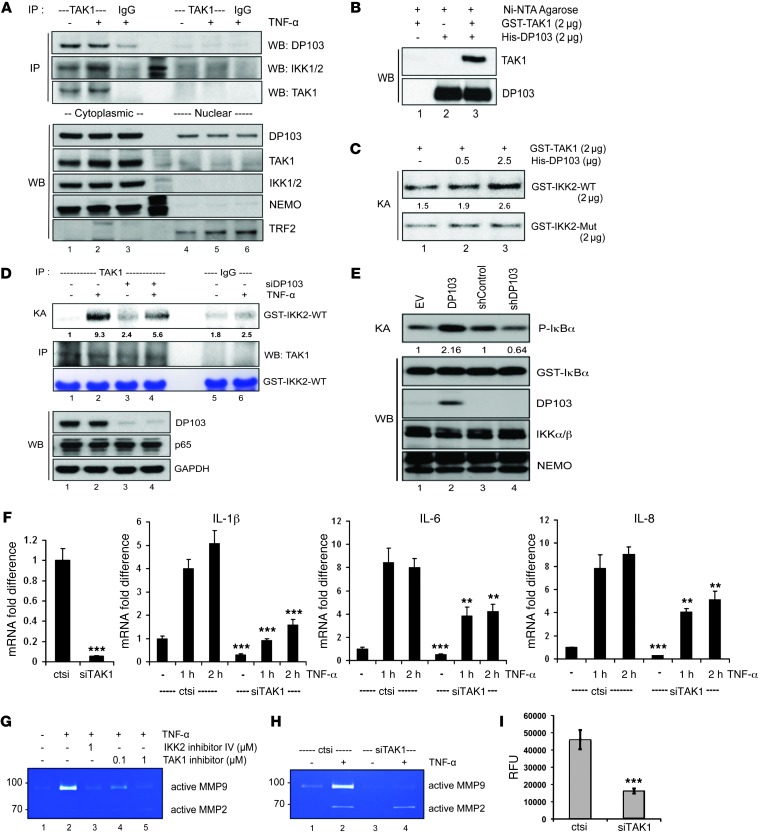
Figure 7. DP103 is a positive cofactor of TAK1-mediated IKK2 activation in MDA-MB-231 cells.
(A) Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions immunoprecipitated with TAK1 and IgG control antibodies and immunoprecipitate material and lysates analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) GST-TAK1 and His-DP103 incubated either separately or together. Immunoprecipitates analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) Kinase assay performed using GST-TAK1 either with GST-IKK2-WT or GST-IKK2-Mut substrates with increasing input of His-DP103 protein. (D) Cells transfected either with control siRNA or siDP103 and stimulated with TNF-α. Lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-TAK1 antibody, and kinase assay was performed using GST–IKK2 (amino acid residues 152–204) as substrate (top panel). (E) Cells transfected with DP103, siDP103, and respective control vectors. IKK complex immunoprecipitated with anti-NEMO antibody. IKK activity was determined using phosphorylation of IκBα. (F) Cells transfected either with control siRNA or siTAK1 and stimulated with TNF-α. Total RNA analyzed for mRNA expression of NF-κB target genes. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (G) Cells treated with IKK2 inhibitor IV or TAK1 inhibitor (5Z)-7-oxozeaenol and stimulated with TNF-α. MMP9 activity evaluated with zymography. (H) Cells treated with control siRNA (ctsi) or siRNAs against TAK1 (siTAK1) and stimulated with TNF-α. MMP9 activity evaluated with zymography. (I) Cells transfected either with control siRNA or siRNAs against TAK1. Invaded cells through Matrigel detached and lysed in assay buffer were presented as relative fluorescence units (RFU). ***P < 0.001. Fold differences in protein expression are indicated in C–E.