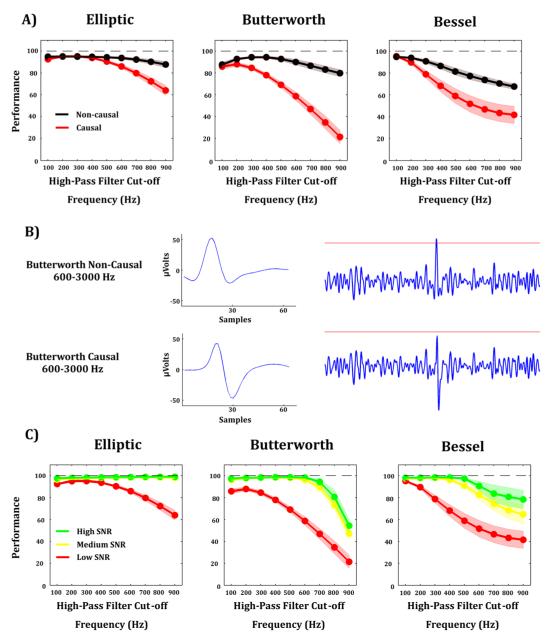
Figure 2. Effect of filtering on spike detection.
A) For different high-pass cut-off frequencies, non-causal filters (black line) lead to better spike detection performance than causal filters (red line) for the Elliptic (left panel), Butterworth (center panel), and Bessel (right panel) filters. These results are based on the simulations with low SNR. B) Illustration of phase distortion effects introduced by causal filters. For a given threshold value, the spike obtained with the non-causal filter is detected (top-right panel) whereas the spike obtained with the causal filter is not (low-right panel). C) For different SNRs, higher cut-off frequencies of the high-pass filter lead to worse spike detection for the Elliptic (left panel), Butterworth (center panel), and Bessel (right panel) filters.