Abstract
Lymphoid cells from A/J and BALB/c strains of mice were iodinated with 125I by the lactoperoxidase method and the plasma membranes were disrupted by freezing and thawing or with 0.5 percent Nonidet P-40, a nonionic detergent. Attempts to find choleragen reactive iodinated material in 0.5 percent Nonidet P-40 lysates were unsuccessful even when the cells were incubated with choleragen before lysis. Freezing and thawing the cells resulted in the release of iodinated choleragen reactive material. The interaction of choleragen with the iodinated material could be inhibited (at low choleragen concentrations) or enhanced (at high choleragen concentrations) by the addition of the ganglioside G-M1 to the the immune precipitation system. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that the receptor for choleragen is a glycolipid and reduce, but do not totally eliminate, the likelihood that the receptor is glycoprotein in nature.
Full text
PDF

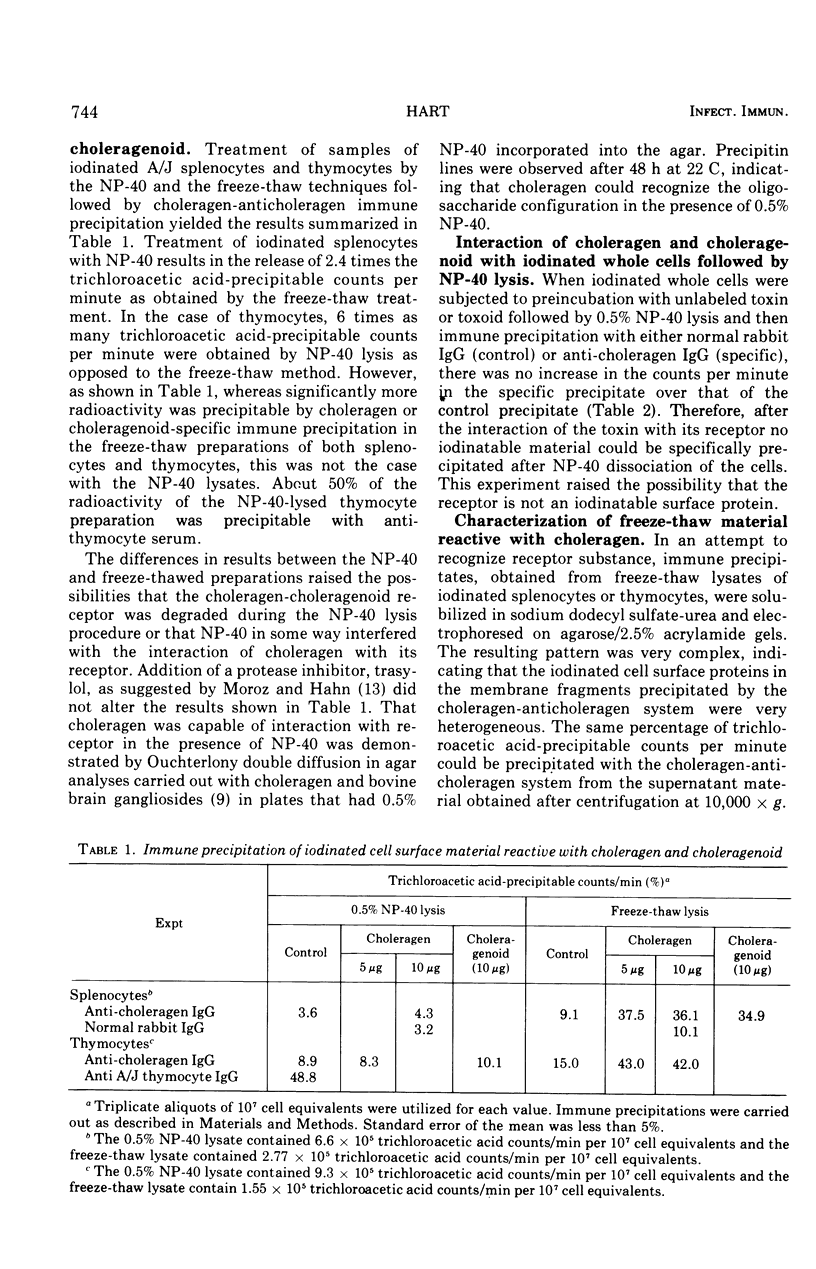
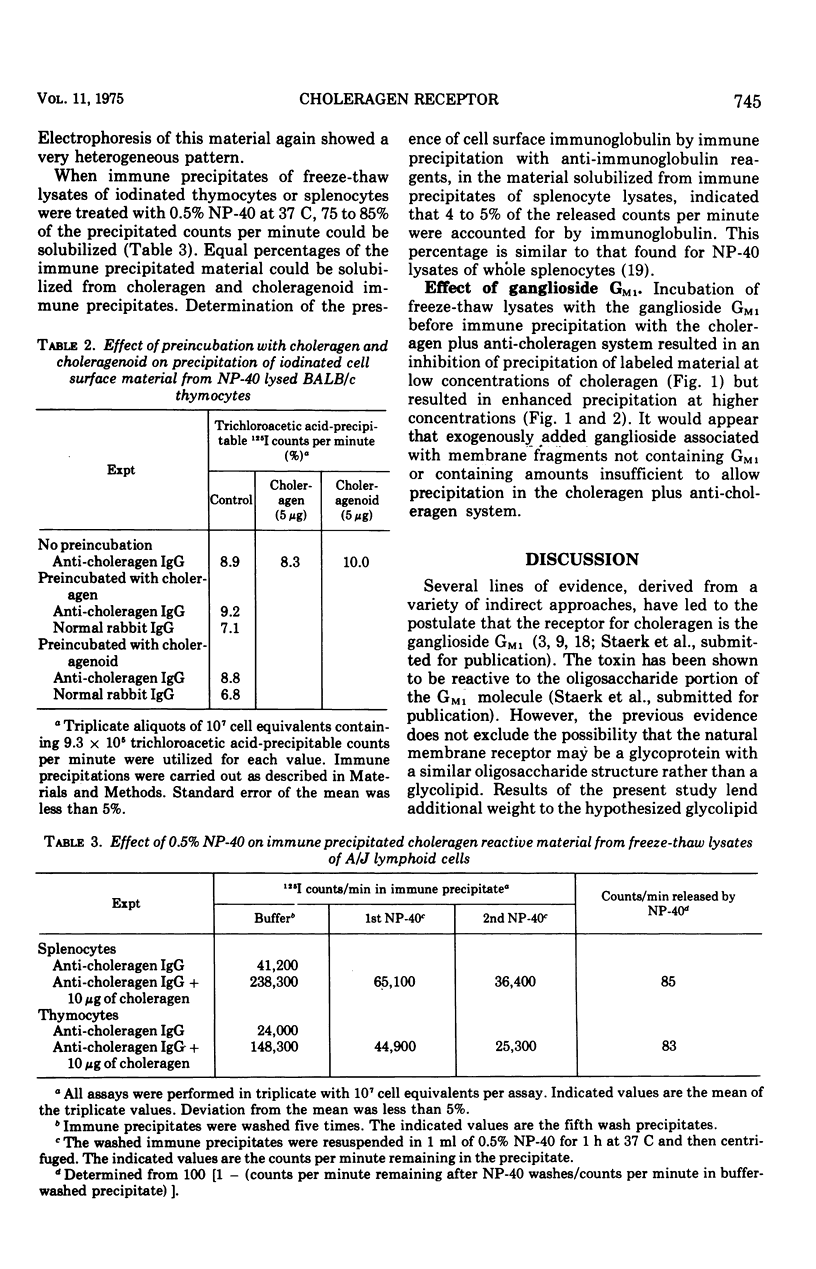
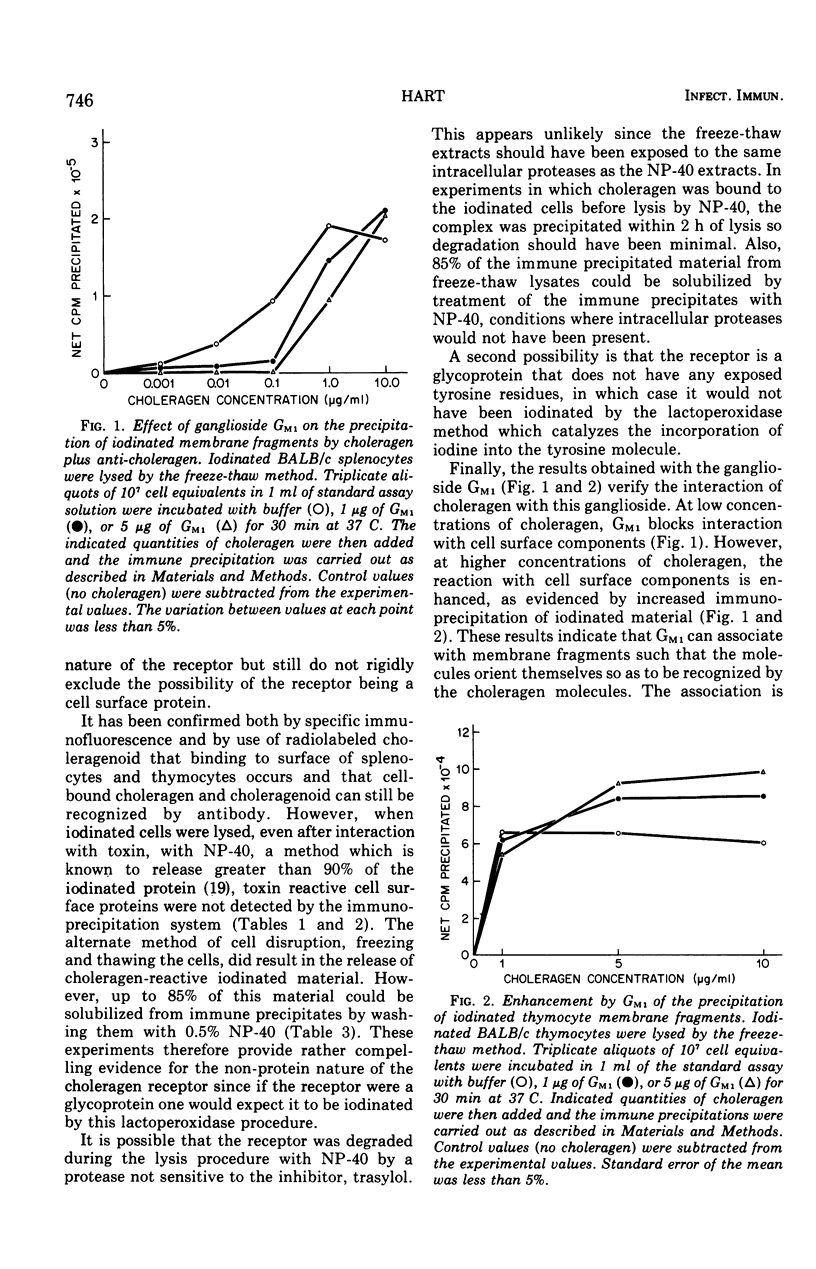

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baur S., Vitetta E. S., Sherr C. J., Schenkein I., Uhr J. W. Isolation of heavy and light chains of immunoglobulin from the surfaces of lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1133–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Melmon K. L., Henney C. S., Weinstein Y., Shearer G. M. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by cyclic AMP. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):19–28. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esselman W. J., Miller H. C. Brain and thymus lipid inhibition of antibrain-associated theta-cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):445–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. I. Binding properties and interference with lectin-induced cellular stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):801–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E. Biochemical and biological characteristics of lymphocyte surface immunoglobulin. Transplant Rev. 1973;14:3–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz C., Hahn Y. Cell-surface immunoglobulin human thymus cells and its biosynthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3716–3720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINDERKNECHT H. Ultra-rapid fluorescent labelling of proteins. Nature. 1962 Jan 13;193:167–168. doi: 10.1038/193167b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Baur S., Grundke I., Zeligs J., Zeligs B., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. 3. Isolation and characterization of immunoglobulin from nonsecretory human lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1392–1405. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Craig J. P. Cholera toxin inhibits macromolecular synthesis in mouse spleen cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):178–180. doi: 10.1038/newbio244178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E., Carpenter C. C., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Deactivation of cholera toxin by ganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):415–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Baur S., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of immunoglobulin from mouse splenic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):242–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W., Boyse E. A. Metabolism of H-2 and Thy-1 (theta) alloantigens in murine thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Apr;4(4):276–282. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Synthesis, transport, dynamics and fate of cell surface Ig and alloantigens in murine lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1973;14:50–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


