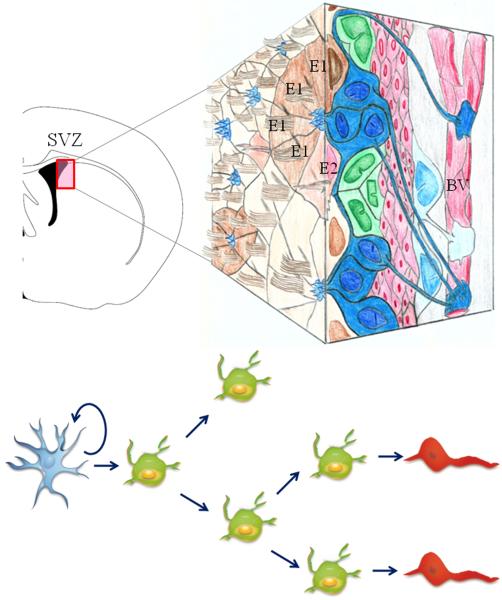
Figure 1.
The adult subventricular zone (SVZ) is lining the striatal wall of the lateral ventricles in the brain (coronal section left). A 3-D model of the SVZ is shown to the right. This region contains astrocytic neural stem cells (type-B cells depicted in blue). Type-B cells give rise to rapidly dividing intermediate progenitor cells (type-C cells depicted in green), which in turn produce migrating neuroblasts (type-A cells depicted in red). Type-B astrocytes have a long basal process contacting blood vessels (BV) and an apical ending at the ventricle surface. Note the pinwheel-like organization composed of multiciliated (Type-E1) and bi-ciliated (Type-E2) ependymal cells encircling apical surfaces of astrocytes. Reprinted from Brain Research Reviews, Vol 67, Gonzalez-Perez & Alvarez-Buylla, Oligodendrogenesis in the subventricular zone and the role of epidermal growth factor, page 148, Copyright 2011, with permission from Elsevier.