Figure 2.
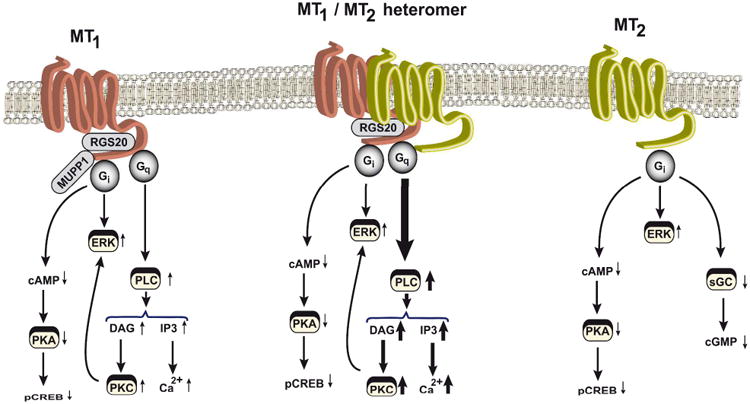
Principal melatonin-receptor signaling pathways. Depending on the type of melatonin-receptor complexes present in cells (MT1 homomers, MT2 homomers, or MT1/MT2 heteromers), the depicted signaling pathways are activated upon melatonin stimulation. Thickness of the arrows represents the potency and efficiency of the activation of the pathway. DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IP3, inositol triphosphate; MUPP1, multi-PDZ domain protein 1; pCREB, phospho-cAMP-response element-binding protein; PLC, phospholipase C; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; RGS20, regulator of G protein signaling 20; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase.
