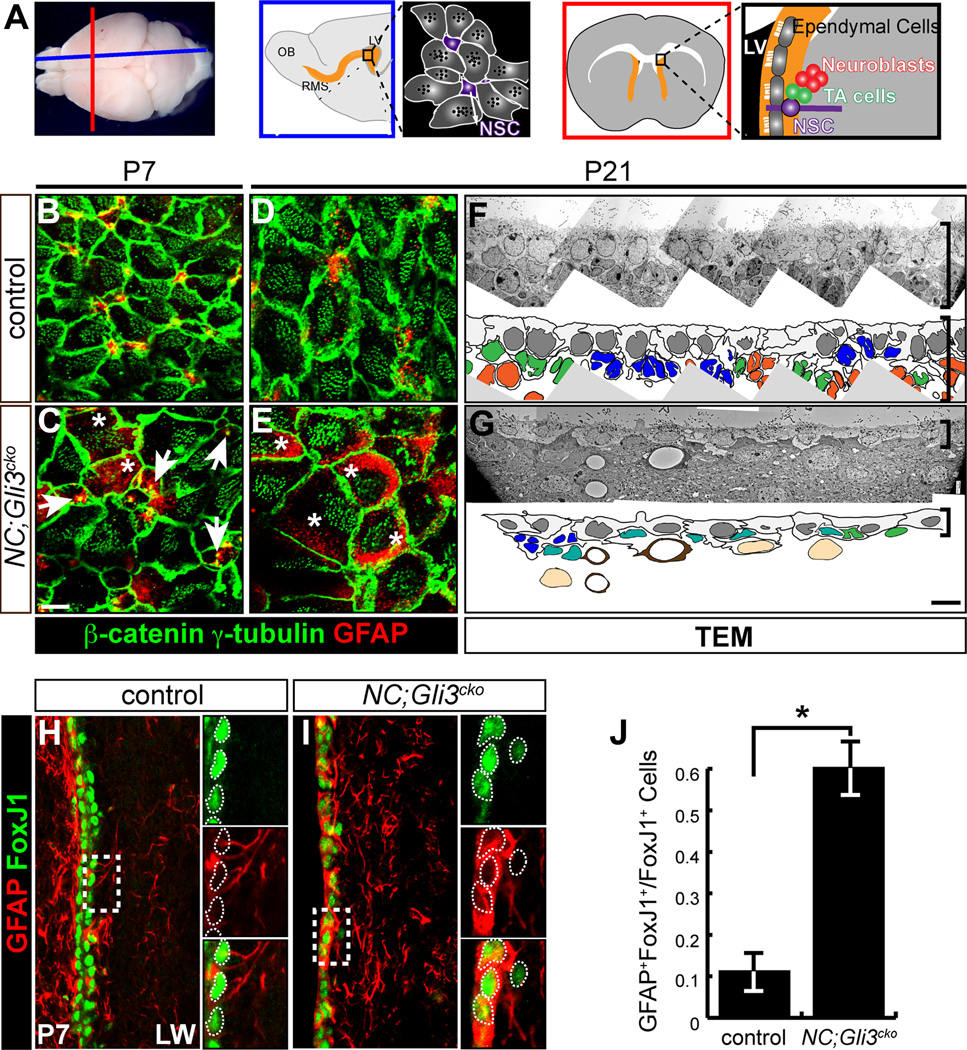
Figure 1. Gli3 is required for proper establishment of the neurogenic niche in the subventricular zone.
(A) Schematics of mouse brain cut along the sagittal (blue) and coronal (red) orientation show the arrangement of cell types found in the neurogenic subventricular zone (SVZ) including neural stem cells (NSCs), transit-amplifying (TA) cells, ependymal cells, and neuroblasts. LV, lateral ventricle; OB, olfactory bulb; RMS, rostral migratory stream.
(B–E) en face view of the lateral wall of the ventricle shows that the pinwheel-like arrangements of ependymal cells (β-catenin+, green cell border; γ-tubulin+, green dots) and neural stem cells (GFAP+, red) are established by P7 in the controls (B and D). NC;Gli3cko mutants that lack Gli3 function in embryonic radial glia cells show persistence of radial glia cells with a single basal body (white arrows) and no clear pinwheel arrangements and ectopic expression of GFAP within β-catenin+ γ-tubulin+ cells (C and E, white asterisks). Scale bar, 5µm.
(F and G) Transmission Electron Micrograph (TEM) analysis of the control (F) and NC;Gli3cko mutants (G). Disrupted cytoarchitecture of the SVZ is shown in the mutants. The SVZ cell types are indicated in colors: blue (NSC); green (TA cell); orange (neuroblast); gray (ependymal cell); teal (atypical cells); light brown (striatal neurons). Brackets indicate the thickness of the SVZ. Scale bar, 5µm.
(H–J) Immunohistochemistry of FoxJ1 (green) and GFAP (red) staining in control (H) and NC;Gli3cko (I) SVZ at P7. FoxJ1 expression is similar between control and NC;Gli3cko SVZ, but many more cells co-express GFAP and FoxJ1 in the NC;Gli3cko mutant (I) as compared to the control (H, quantified in J). Insets reveal co-localization of FoxJ1 and GFAP, with white dashed lines encircling FoxJ1+ cells. Scale bar, 10µm. *, p < 0.05.
See also Figure S1.