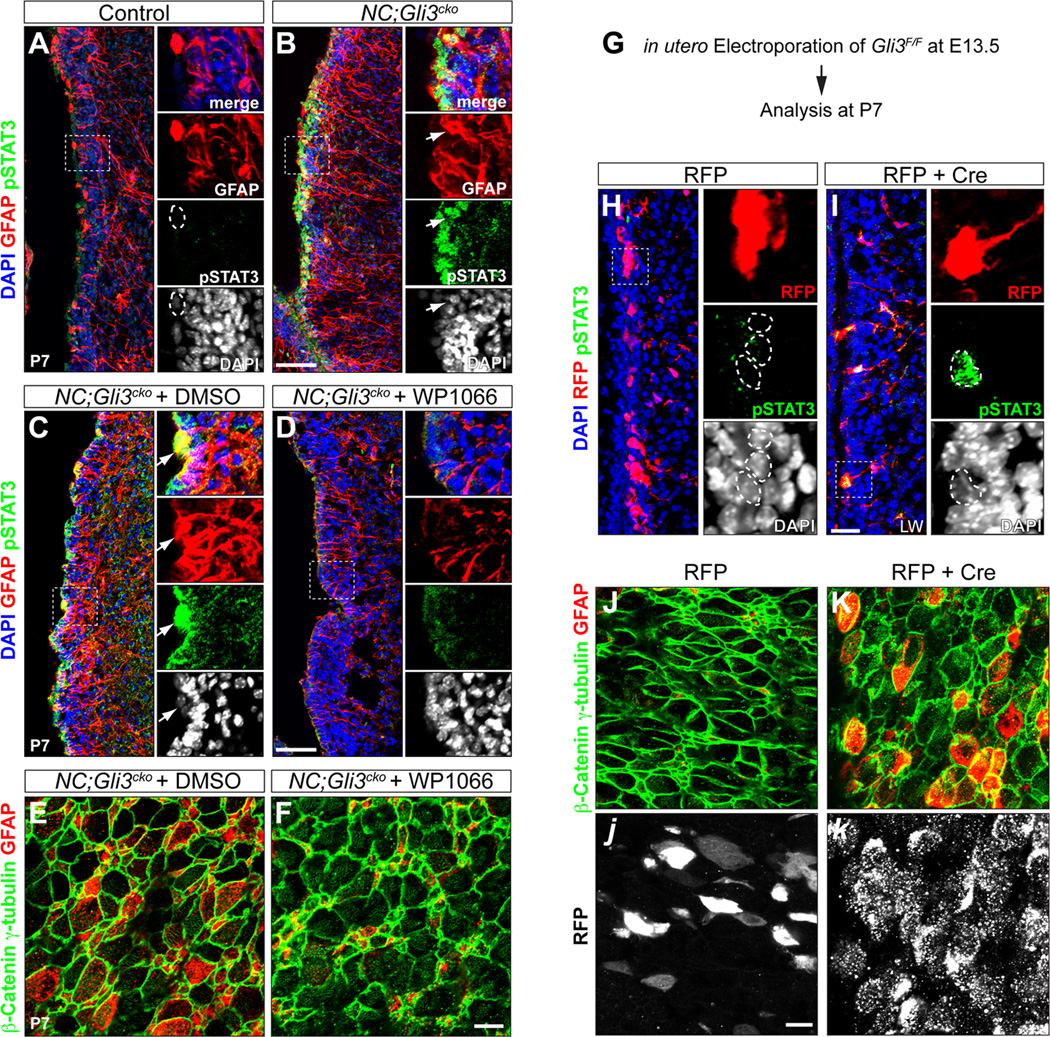
Figure 3. Loss of Gli3 leads to the overactivation of STAT3 and ectopic GFAP expression in NC;Gli3cko mutant SVZ.
(A and B) Immunohistochemistry of phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) and GFAP in control and NC;Gli3cko SVZ at P7. Both pSTAT3 (green) and GFAP (red) are increased in NC;Gli3cko (B) compared to control (A). Higher magnification images of boxed areas are shown in right panels. GFAP+ cell (outlined by dashed circle) does not express pSTAT3 in the control. Arrows indicate the GFAP+ cell expresses a high level of nuclear pSTAT3 in the mutant. Scale bar, 50µm.
(C and D) NC;Gli3cko embryos received either STAT3 inhibitor (WP1066) or vehicle control DMSO from E16.5 till birth. The animals were analyzed at P7. The nuclear pSTAT3 (green) in GFAP+ (red) cells shown in mutants receiving DMSO (C) is rescued by WP1066 (D). Arrows indicate the GFAP+ cell expresses a high level of nuclear pSTAT3 in the DMSO treated mutant.
(E and F) en face view of P7 NC;Gli3cko SVZ which were treated with either STAT3 inhibitor (WP1066) or vehicle control DMSO prenatally. The ectopic GFAP expression (red) in ependymal-like cells (β-catenin+ γ-tubulin+, green) in NC;Gli3cko treated with DMSO (E) is rescued by WP1066 (F). Scale bar, 50µm.
(G–K) in utero electroporation of either RFP alone or RFP + Cre into Gli3F/F embryos. Electroporation was done at E13.5 and the manipulated pups were sacrificed at P7. The Gli3 mutant cells induced by Cre are labeled by RFP in (I). The electroporated cells received RFP alone (red) does not have nuclear pSTAT3 (green) expression (indicated by dashed circles in H). However, the Gli3 mutant cells (red) express nuclear pSTAT3 (green) (indicated by dashed circles in I). Scale bar, 25 µm. en face view shows that Gli3 mutant cells (white in k) exhibit ectopic GFAP expression (red in K) in ependymal-like cells (β-catenin+ γ-tubulin+, green). The ectopic GFAP expression is absent in cells that received RFP alone (white in j). Scale bar, 50µm.
See also Figure S3.